2주차 공유 시작하겠습니다.
데이터 소스
- 데이터 소스는 테라폼으로 정의되지 않은 외부 리소스 또는 저장된 정보를 테라폼 내에서 참조할 때 사용한다
- 데이터 소스 블록은 data 로 시작, 이후 ‘데이터 소스 유형’을 정의 ← Resource 블록 정의와 유사
- 데이터 소스 유형은 첫 번째 _를 기준으로 앞은 프로바이더 이름, 뒤는 프로바이더에서 제공하는 리소스 유형을 의미한다.
- 데이터 소스 유형을 선언한 뒤에는 고유한 이름을 붙인다. 리소스의 이름과 마찬가지로 이름은 동일한 유형에 대한 식별자 역할을 하므로 중복될 수 없다.
- 이름 뒤에는 데이터 소스 유형에 대한 구성 인수들은 { } 안에 선언한다. 인수가 필요하지 않은 유형도 있지만, 그때에도 { } 는 입력한다
data "local_file" "abc" {
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
# 실습 확인을 위해서 abc.txt 파일 생성
echo "t101 study - 2week" > abc.txt
#
terraform init && terraform plan && terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
# 테라폼 콘솔 : 데이터 소스 참조 확인
terraform console
>
data.local_file.abc
...
data.local_file.abc.filename
data.local_file.abc.content
data.local_file.abc.id
exit
확인

데이터 소스로 읽은 대상을 참조하는 방식은 리소스와 구별되게 data가 앞에 붙는다. 속성 값은 다음과 같이 접근할 수 있다.
# Terraform Code
data "<리소스 유형>" "<이름>" {
<인수> = <값>
}
# 데이터 소스 참조
data.<리소스 유형>.<이름>.<속성>
ex
# Declare the data source
data "aws_availability_zones" "available" {
state = "available"
}
resource "aws_subnet" "primary" {
availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.available.names[0]
# e.g. ap-northeast-2a
}
resource "aws_subnet" "secondary" {
availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.available.names[1]
# e.g. ap-northeast-2b
}
예시 코드 확인 - AZ datasource - 링크
data "aws_availability_zones" "seoul" {
state = "available"
}
확인

[도전과제1] 위 리전 내에서 사용 가능한 가용영역 목록 가져오기를 사용한 VPC 리소스 생성 실습 진행, 혹은 아무거나 데이터 소스를 사용한 실습 진행
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = "123!"
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
data "local_file" "abc" {
filename = local_file.abc.filename
}
resource "local_file" "def" {
content = data.local_file.abc.content
filename = "${path.module}/def.txt"
}
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
# 파일 확인
ls *.txt
diff abc.txt def.txt
# graph 확인
terraform graph > graph.dot
# 테라폼 콘솔 : 데이터 소스 참조 확인
echo "data.local_file.abc.content" | terraform console
# 생성된 파일 권한이 다름??? 왜지???
ls -l
확인

입력변수 Variable
입력 변수는 인프라를 구성하는 데 필요한 속성 값을 정의해 코드의 변경 없이 여러 인프라를 생성하는 데 목적이 있다.
테라폼에서는 이것을 입력 변수 Input Variables 로 정의한다.
- 변수는 variable로 시작되는 블록으로 구성된다. 변수 블록 뒤의 이름 값은 동일 모듈 내 모든 변수 선언에서 고유해야 하며, 이 이름으로 다른 코드 내에서 참조된다.
# variable 블록 선언의 예
variable "<이름>" {
<인수> = <값>
}
variable "image_id" {
type = string
}
- 변수 정의 시 사용 가능한 메타인수
- default : 변수 값을 전달하는 여러 가지 방법을 지정하지 않으면 기본값이 전달됨, 기본값이 없으면 대화식으로 사용자에게 변수에 대한 정보를 물어봄
- type : 변수에 허용되는 값 유형 정의, string number bool list map set object tuple 와 유형을 지정하지 않으면 any 유형으로 간주
- description : 입력 변수의 설명
- validation : 변수 선언의 제약조건을 추가해 유효성 검사 규칙을 정의 - 링크
- sensitive : 민감한 변수 값임을 알리고 테라폼의 출력문에서 값 노출을 제한 (암호 등 민감 데이터의 경우) - 링크
- nullable : 변수에 값이 없어도 됨을 지정 - Link
변수 유형별 선언 방식의 예시 - main.tf 파일
variable "string" {
type = string
description = "var String"
default = "myString"
}
variable "number" {
type = number
default = 123
}
variable "boolean" {
default = true
}
variable "list" {
default = [
"google",
"vmware",
"amazon",
"microsoft"
]
}
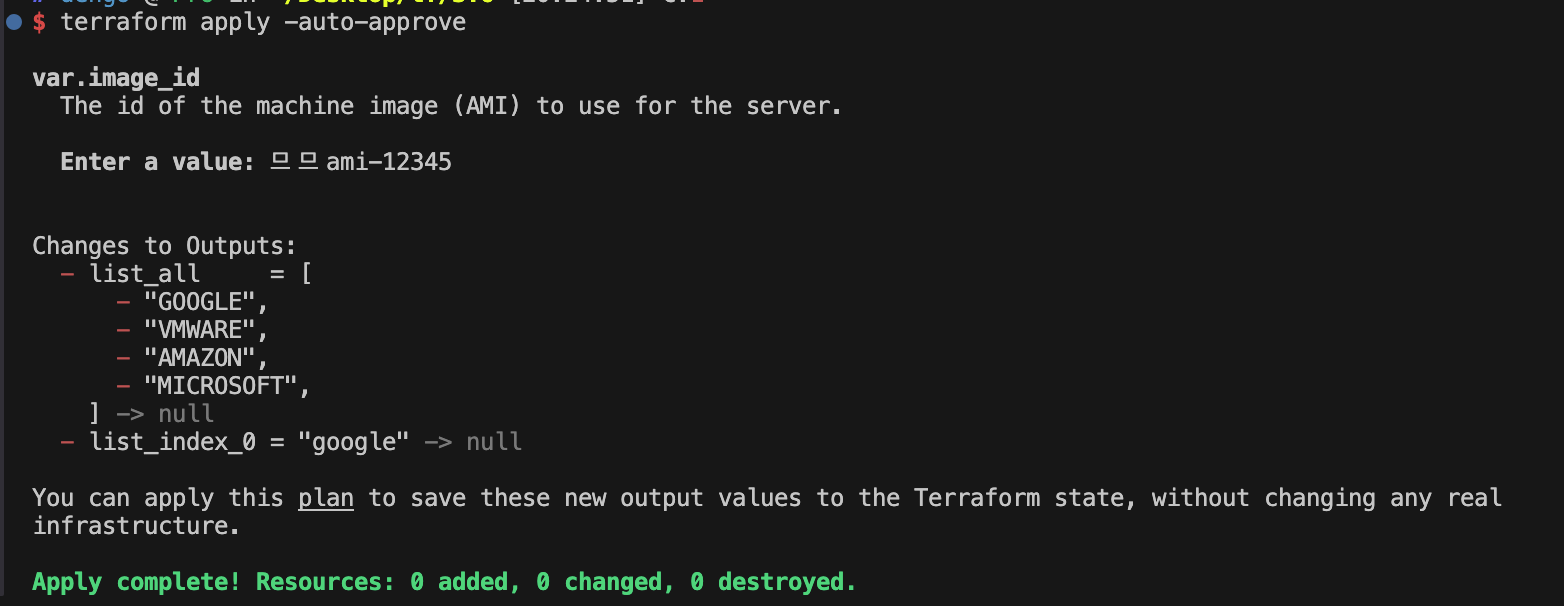
output "list_index_0" {
value = var.list.0
}
output "list_all" {
value = [
for name in var.list : upper(name)
]
}
variable "map" { # Sorting
default = {
aws = "amazon",
azure = "microsoft",
gcp = "google"
}
}
variable "set" { # Sorting
type = set(string)
default = [
"google",
"vmware",
"amazon",
"microsoft"
]
}
variable "object" {
type = object({ name = string, age = number })
default = {
name = "abc"
age = 12
}
}
variable "tuple" {
type = tuple([string, number, bool])
default = ["abc", 123, true]
}
variable "ingress_rules" { # optional ( >= terraform 1.3.0)
type = list(object({
port = number,
description = optional(string),
protocol = optional(string, "tcp"),
}))
default = [
{ port = 80, description = "web" },
{ port = 53, protocol = "udp" }]
}
#
terraform init && terraform plan && terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
#
terraform output
list_all = [
"GOOGLE",
"VMWARE",
"AMAZON",
"MICROSOFT",
]
list_index_0 = "google"
확인

유효성 검사
- 유효성 검사 : 입력되는 변수 타입 지징 이외, 사용자 지정 유효성 검사가 가능
- 변수 블록 내에 validation 블록에서 조건인 condition에 지정되는 규칙이 true 또는 false를 반환해야 하며, error_message는 condition 값의 결과가 false 인 경우 출력되는 메시지를 정의한다.
- regex 함수는 대상의 문자열에 정규식을 적용하고 일치하는 문자열을 반환하는데, 여기에 can 함수를 함께 사용하면 정규식에 일치하지 않는 경우의 오류를 검출한다.
- validation 블록은 중복으로 선언할 수 있다.
- variable 유효성 검사의 예
variable "image_id" {
type = string
description = "The id of the machine image (AMI) to use for the server."
validation {
condition = length(var.image_id) > 4
error_message = "The image_id value must exceed 4."
}
validation {
# regex(...) fails if it cannot find a match
condition = can(regex("^ami-", var.image_id))
error_message = "The image_id value must starting with \"ami-\"."
}
}
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
var.image_id
The id of the machine image (AMI) to use for the server.
Enter a value: ami
...
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
var.image_id
The id of the machine image (AMI) to use for the server.
Enter a value: ami-
...
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
var.image_id
The id of the machine image (AMI) to use for the server.
Enter a value: ami-12345678
...
terraform apply -auto-approve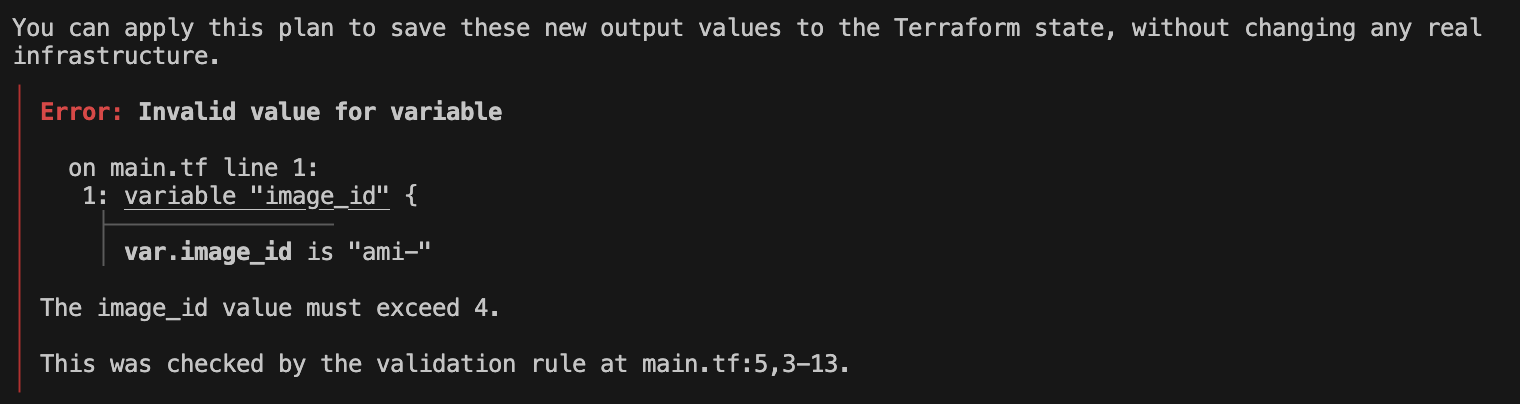
ami-1234로 다시 입력
변수 참조 : variable은 코드 내에서 var.<이름>으로 참조된다.
variable "my_password" {}
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = var.my_password
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
#
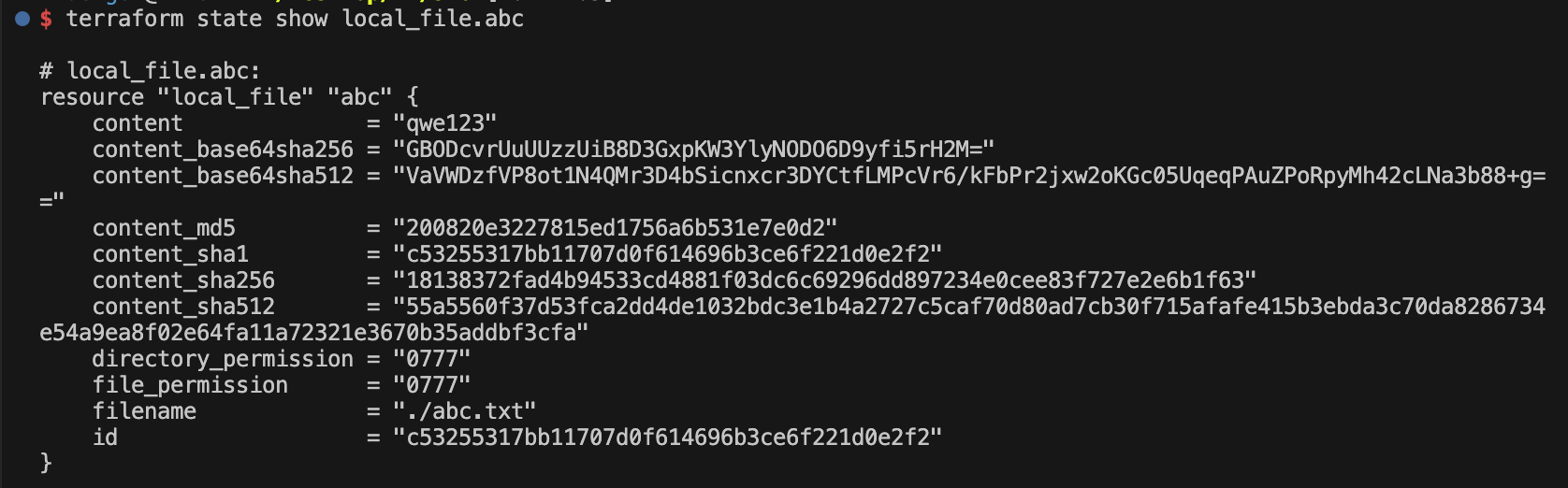
terraform init -upgrade && terraform apply -auto-approve
var.my_password
Enter a value: qwe123
...
# 확인
terraform state list
terraform state show local_file.abc
cat abc.txt ; echo
# 해당 파일에 다른 내용으로 변경해보기
terraform apply -auto-approve
var.my_password
Enter a value: t101mypss
...
# 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo
민감한 변수 취급 : 입력 변수의 민감 여부 선언 가능
기본값 추가로 입력 항목은 발생하지 않지만, 출력에서 참조되는 변수 값이(sensitive)로 감춰지는 것을 확인 할 수 있다
variable "my_password" {
default = "password"
sensitive = true
}
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = var.my_password
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
-확인 : 민감한 변수로 지정해도 terraform.tfstate 파일에는 결과물이 평문으로 기록되므로 State 파일의 보안에 유의해야 한다
# 출력부분에 내용 안보임!
terraform apply -auto-approve
...
~ content = (sensitive value)
...
terraform state show local_file.abc
echo "local_file.abc.content" | terraform console
(sensitive value)
# 결과물 파일 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo
# terraform.tfstate 파일 확인 : VSCODE에서 terraform.tfstate 클릭 후 확인
cat terraform.tfstate | grep '"content":'
"content": "password",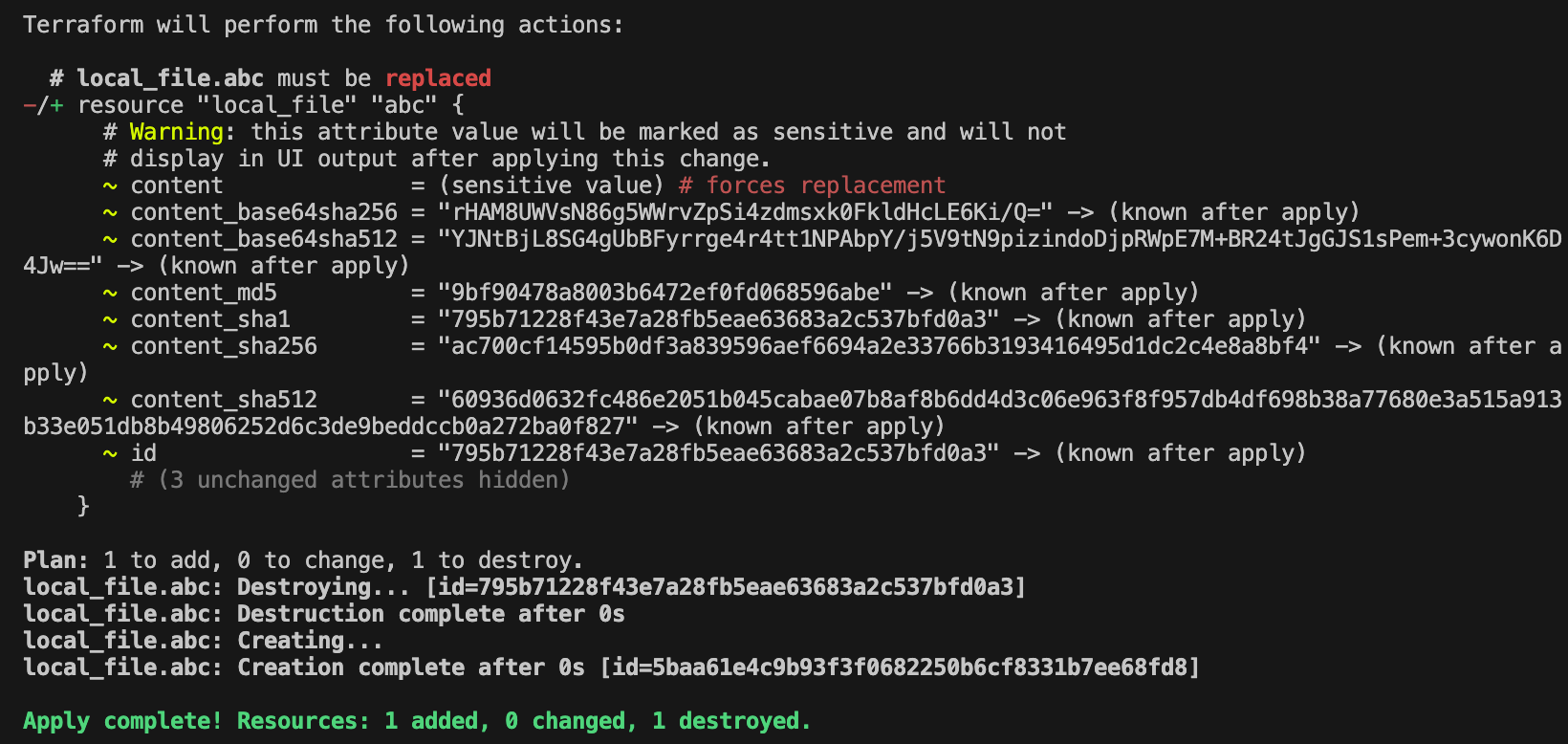
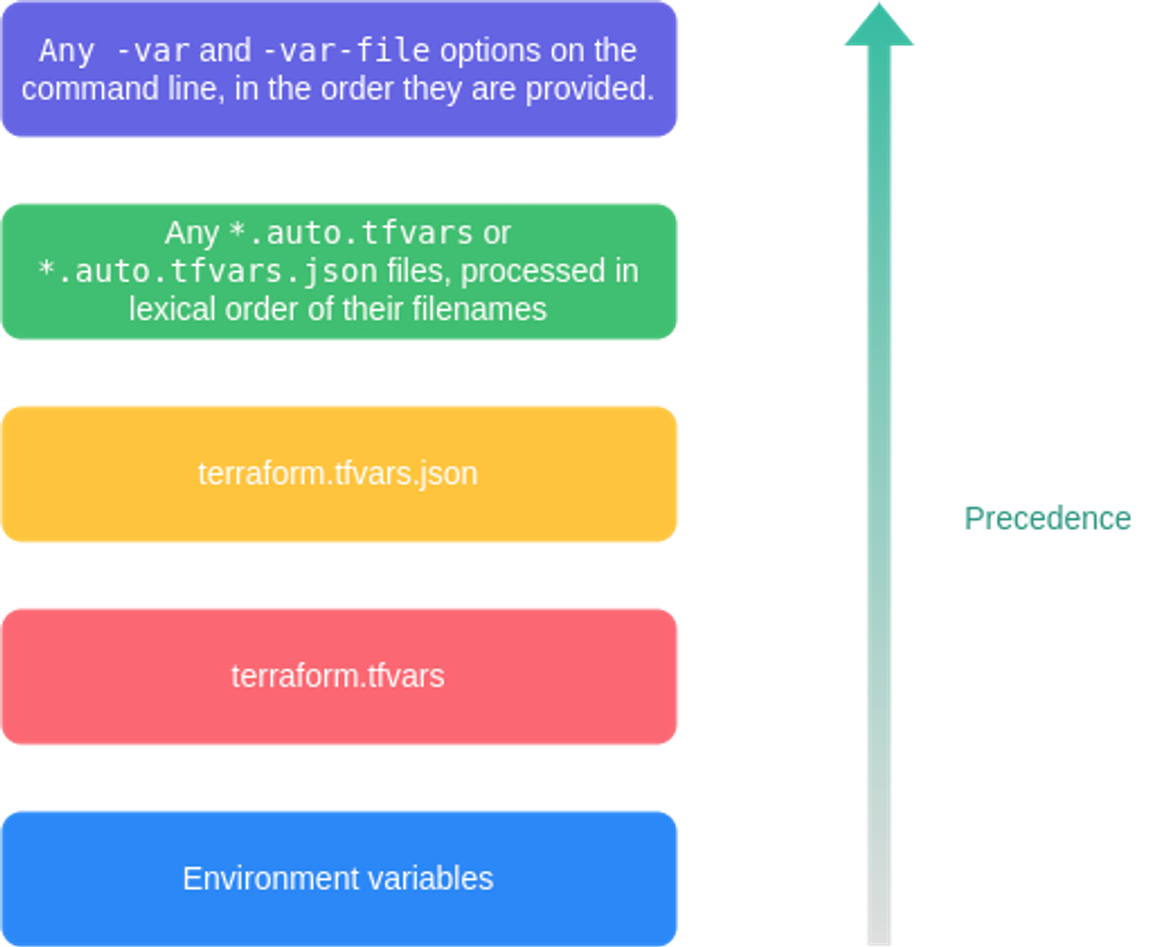
변수 입력 방식과 우선순위
- variable의 목적은 코드 내용을 수정하지 않고 테라폼의 모듈적 특성을 통해 입력되는 변수로 재사용성을 높이는 데 있다.
- 특히 입력 변수라는 명칭에 맞게 사용자는 프로비저닝 실행 시에 원하는 값으로 변수에 정의할 수 있다.
- 선언되는 방식에 따라 변수의 우선순위가 있으므로, 이를 적절히 사용해 로컬 환경과 빌드 서버 환경에서의 정의를 다르게 하거나, 프로비저닝 파이프라인을 구성하는 경우 외부 값을 변수에 지정할 수 있다.
variable "my_var" {}
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = var.my_var
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
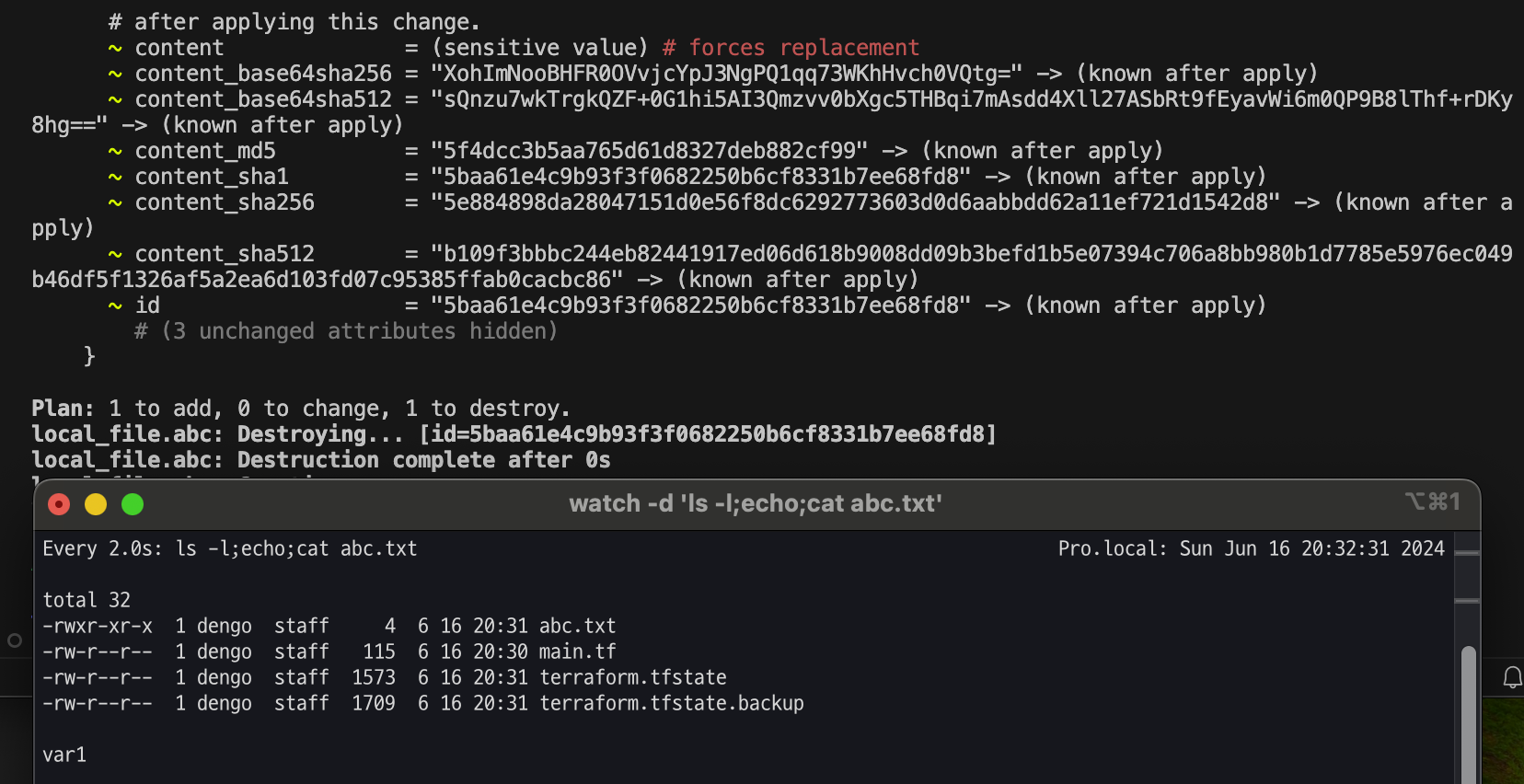
[우선순위 수준 1] 실행 후 입력
# (옵션) 신규 터미널
watch -d 'ls -l;echo;cat abc.txt'
# 실행
terraform apply -auto-approve
var.my_var
Enter a value: var1
...
# 확인
terraform state show local_file.abc
cat abc.txt ; echo
확인
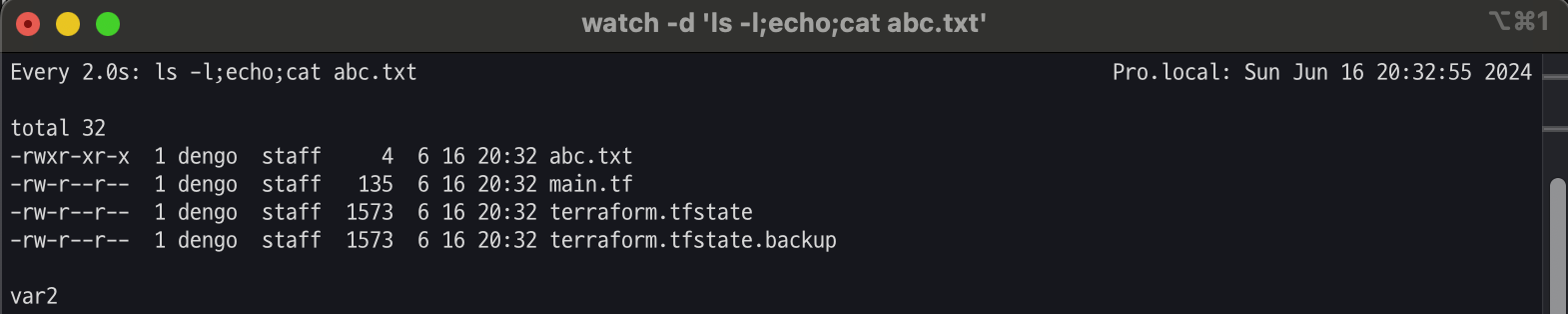
[우선순위 수준 2] variable 블록의 default 값
variable "my_var" {
default = "var2"
}
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = var.my_var
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
[우선순위 수준 3] 환경 변수 (TF_VAR 변수 이름)
- 시스템 환경 변수의 접두사에 TF_VAR_ 가 포함되면 그 뒤의 문자열을 변수 이름으로 인식한다.
- 앞서 default로 추가한 내용과 어떤 방식이 우선순위가 높은지 확인해보자
# Linux/macOS
export TF_VAR_my_var=var3
echo $TF_VAR_my_var
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo
[우선순위 수준 4] terraform.tfvars에 정의된 변수 선언
- 루트 모듈의 main.tf 파일과 같은 위치에 terraform.tfvars 파일을 생성해 변수에 대한 값을 추가하고 앞서 선언한 변수 선언과 비교해 우선순위를 확인
#
echo 'my_var="var4"' > terraform.tfvars
cat terraform.tfvars
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo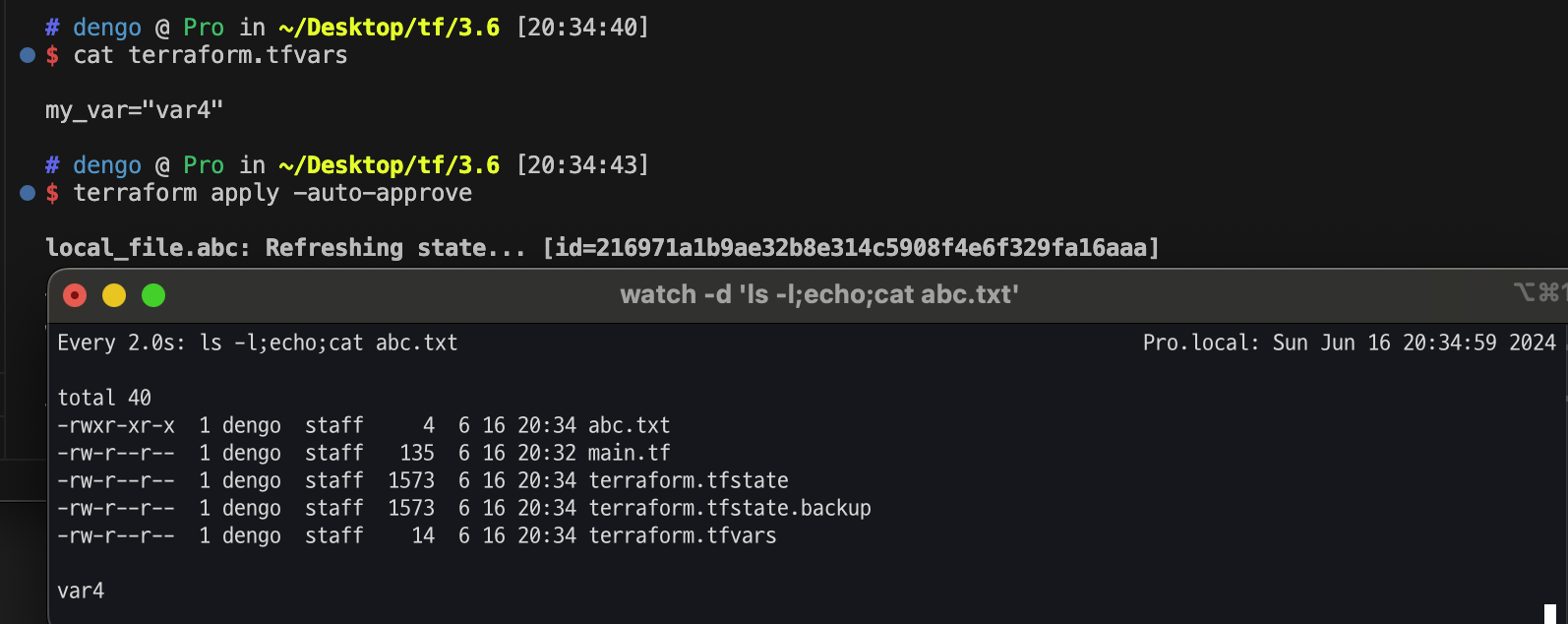
[우선순위 수준 5] *.auto.tfvars에 정의된 변수 선언
- 파일명의 정렬에 따라 우선순위가 적용된다
# a.auto.tfvars 파일 생성
echo 'my_var="var5_a"' > a.auto.tfvars
ls *.tfvars
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo
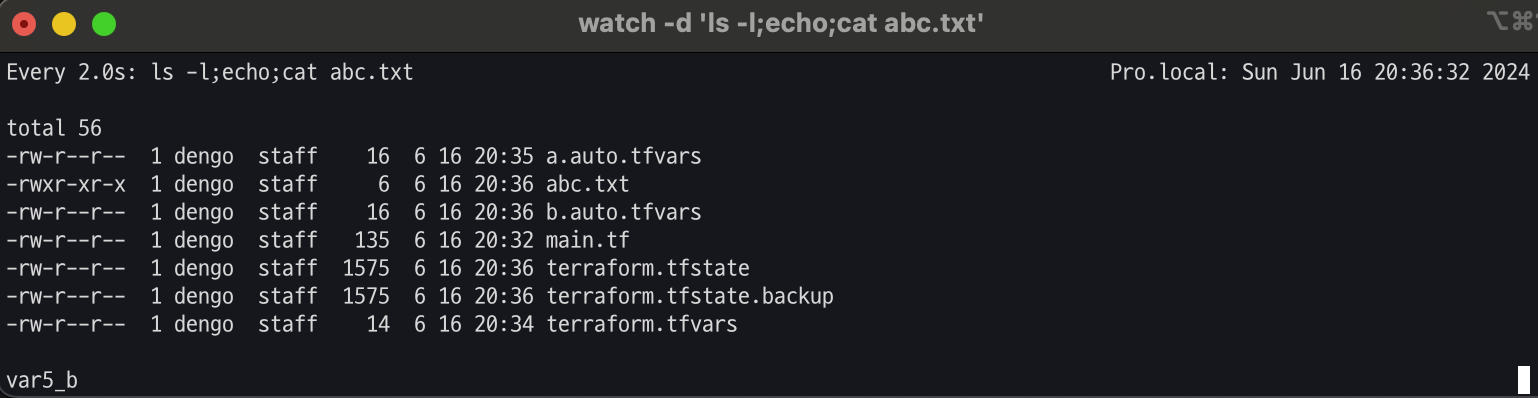
# b.auto.tfvars 파일 생성
echo 'my_var="var5_b"' > b.auto.tfvars
ls *.tfvars
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo
[우선순위 수준 6] *.auto.tfvars.json에 정의된 변수 선언
- *.auto.tfvars와 같이 파일명의 정렬에 따라 우선순위가 적용된다
# a.auto.tfvars.json 파일 생성
cat <<EOF > a.auto.tfvars.json
{
"my_var" : "var6_a"
}
EOF
ls *.tfvars ; ls *.json
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인 >> 결과가 어떻게 되나요?
cat abc.txt ; echo
# c.auto.tfvars.json 파일 생성
cat <<EOF > c.auto.tfvars.json
{
"my_var" : "var6_c"
}
EOF
ls *.tfvars ; ls *.json
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인
cat abc.txt ; echo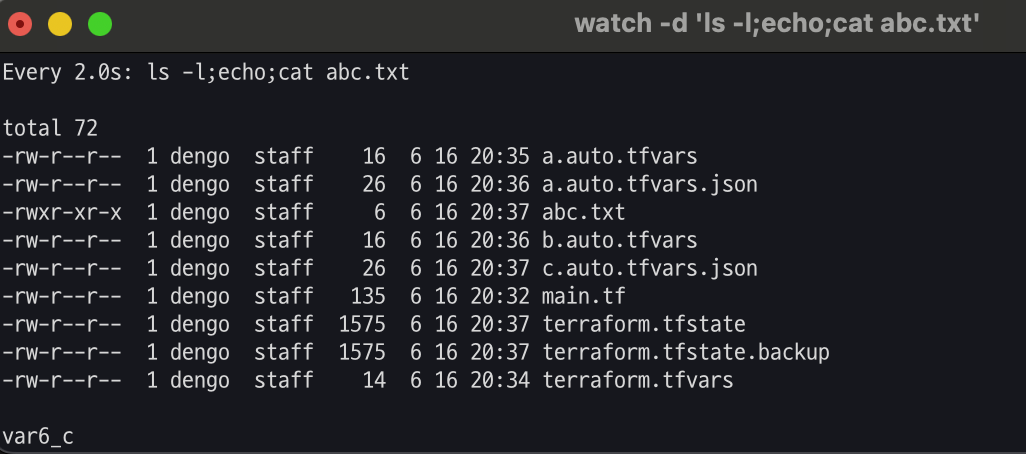
[우선순위 수준 7] CLI 실행 시 -var 인수에 지정 또는 -var-file로 파일 지정
- 여러 인수가 선언되는 경우 나중에 선언된 변수의 우선순위가 높다
#
terraform apply -auto-approve -var=my_var=var7
cat abc.txt ; echo
#
terraform apply -auto-approve -var=my_var=var7 -var=my_var=var8
cat abc.txt ; echo
*.tfvars와 같은 형식의 내용의 파일이라면 -var-file로 지정할 수 있다.
# var9.txt 파일 생성
echo 'my_var="var9"' > var9.txt
#
terraform apply -auto-approve -var=my_var=var7 -var-file="var9.txt"
cat abc.txt ; echo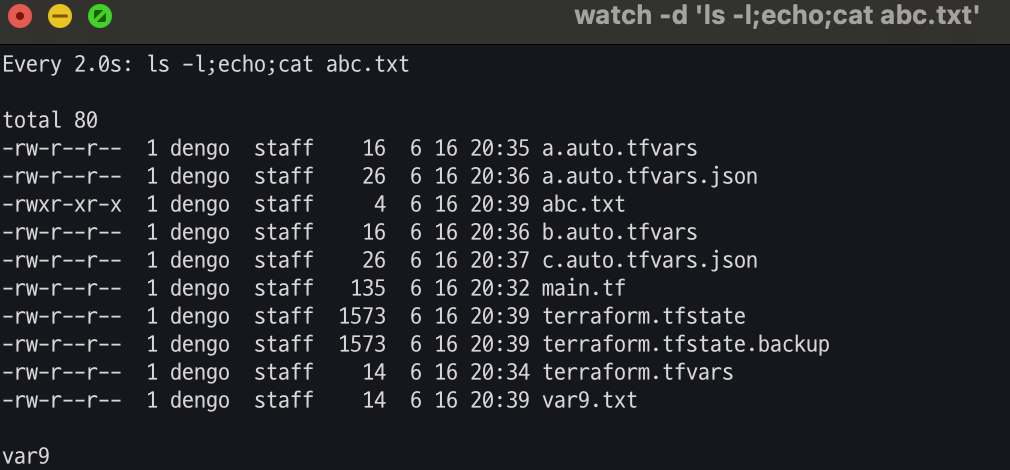
[스터디 전용/실습1] VPC + 보안그룹 + EC2 배포 👍🏻
목표 : default VPC 대신 직접 VPC를 만들고, 해당 VPC내에 EC2 1대를 배포
# 신규 디렉터리 생성
mkdir my-vpc-ec2
cd my-vpc-ec2
touch vpc.tf
##VPC생성
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-2"
}
resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" {
cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/16"
tags = {
Name = "t101-study"
}
}
##
# 배포
terraform init && terraform plan && terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
terraform state show aws_vpc.myvpc
# VPC 확인
export AWS_PAGER=""
aws ec2 describe-vpcs | jq
aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' | jq
aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml
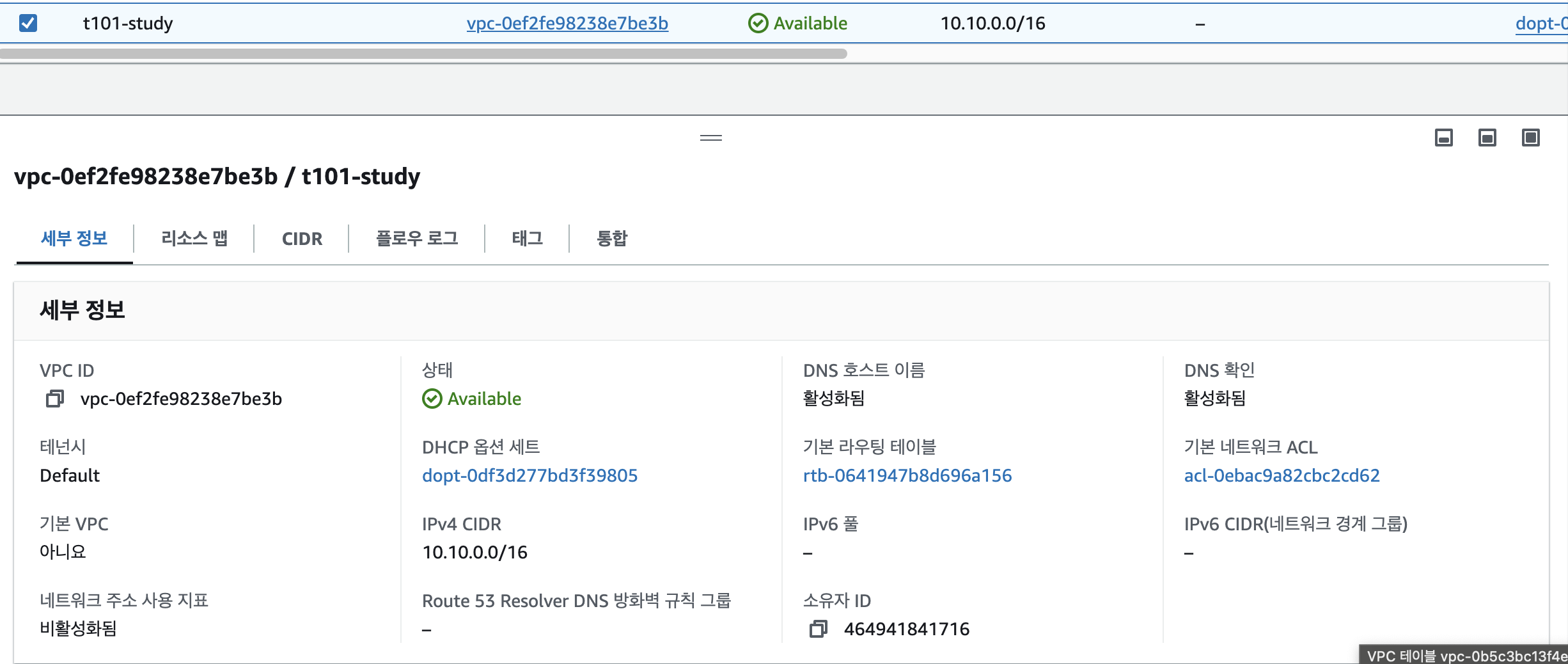
- AWS 관리콘솔에서 VPC 생성 정보 확인 : DNS 옵션값 확인
- vpc.tf 코드 내용 수정 : VPC DNS 옵션 수정
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-2"
}
resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" {
cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = "t101-study"
}
}
확인
vpc.tf 코드 내용 수정 : 서브넷 2개 생성 추가
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-2"
}
resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" {
cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = "t101-study"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mysubnet1" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.1.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-2a"
tags = {
Name = "t101-subnet1"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mysubnet2" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-2c"
tags = {
Name = "t101-subnet2"
}
}
output "aws_vpc_id" {
value = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
}

vpc.tf 코드 내용 수정 : IGW 인터넷 게이트웨이 추가
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-2"
}
resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" {
cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = "t101-study"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mysubnet1" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.1.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-2a"
tags = {
Name = "t101-subnet1"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mysubnet2" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-2c"
tags = {
Name = "t101-subnet2"
}
}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "myigw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
tags = {
Name = "t101-igw"
}
}
output "aws_vpc_id" {
value = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
}
vpc.tf 코드 내용 수정 : IGW 인터넷 게이트웨이로 전달하는 디폴트 라우팅 정보 추가
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-2"
}
resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" {
cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = "t101-study"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mysubnet1" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.1.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-2a"
tags = {
Name = "t101-subnet1"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mysubnet2" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-northeast-2c"
tags = {
Name = "t101-subnet2"
}
}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "myigw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
tags = {
Name = "t101-igw"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table" "myrt" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
tags = {
Name = "t101-rt"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "myrtassociation1" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.mysubnet1.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.myrt.id
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "myrtassociation2" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.mysubnet2.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.myrt.id
}
resource "aws_route" "mydefaultroute" {
route_table_id = aws_route_table.myrt.id
destination_cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.myigw.id
}
output "aws_vpc_id" {
value = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
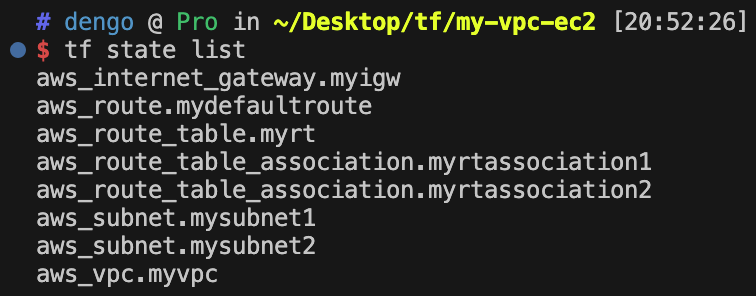
}
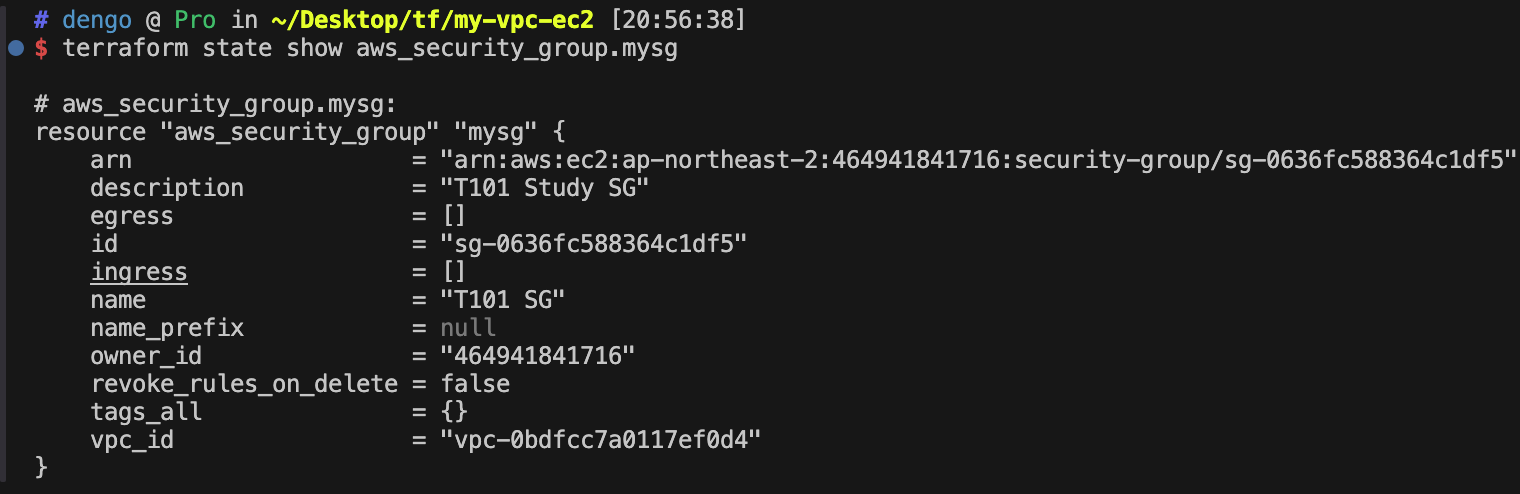
sg.tf 파일 생성 : 보안그룹 생성
resource "aws_security_group" "mysg" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.myvpc.id
name = "T101 SG"
description = "T101 Study SG"
}
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "mysginbound" {
type = "ingress"
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
security_group_id = aws_security_group.mysg.id
}
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "mysgoutbound" {
type = "egress"
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
security_group_id = aws_security_group.mysg.id
}
output "aws_security_group_id" {
value = aws_security_group.mysg.id
}
ec2.tf 파일 생성 : EC2 생성
touch ec2.tf
data "aws_ami" "my_amazonlinux2" {
most_recent = true
filter {
name = "owner-alias"
values = ["amazon"]
}
filter {
name = "name"
values = ["amzn2-ami-hvm-*-x86_64-ebs"]
}
owners = ["amazon"]
}
resource "aws_instance" "myec2" {
depends_on = [
aws_internet_gateway.myigw
]
ami = data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.id
associate_public_ip_address = true
instance_type = "t2.micro"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.mysg.id}"]
subnet_id = aws_subnet.mysubnet1.id
user_data = <<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
wget https://busybox.net/downloads/binaries/1.31.0-defconfig-multiarch-musl/busybox-x86_64
mv busybox-x86_64 busybox
chmod +x busybox
RZAZ=$(curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/placement/availability-zone-id)
IID=$(curl 169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id)
LIP=$(curl 169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4)
echo "<h1>RegionAz($RZAZ) : Instance ID($IID) : Private IP($LIP) : Web Server</h1>" > index.html
nohup ./busybox httpd -f -p 80 &
EOF
user_data_replace_on_change = true
tags = {
Name = "t101-myec2"
}
}
output "myec2_public_ip" {
value = aws_instance.myec2.public_ip
description = "The public IP of the Instance"
}
--확인
#
ls *.tf
terraform plan && terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2
aws_instance.myec2
...
terraform state show data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2
terraform state show aws_instance.myec2
# 데이터소스 값 확인
terraform console
>
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.id
"ami-01c81850a6167bb81"
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.image_id
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.name
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.owners
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.platform_details
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.hypervisor
data.aws_ami.my_amazonlinux2.architecture
exit
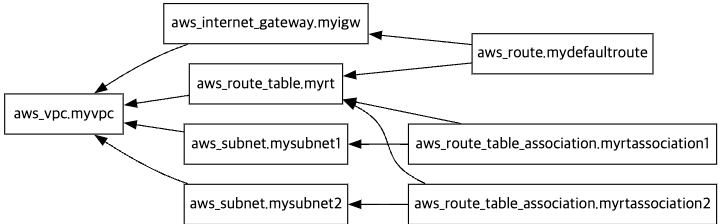
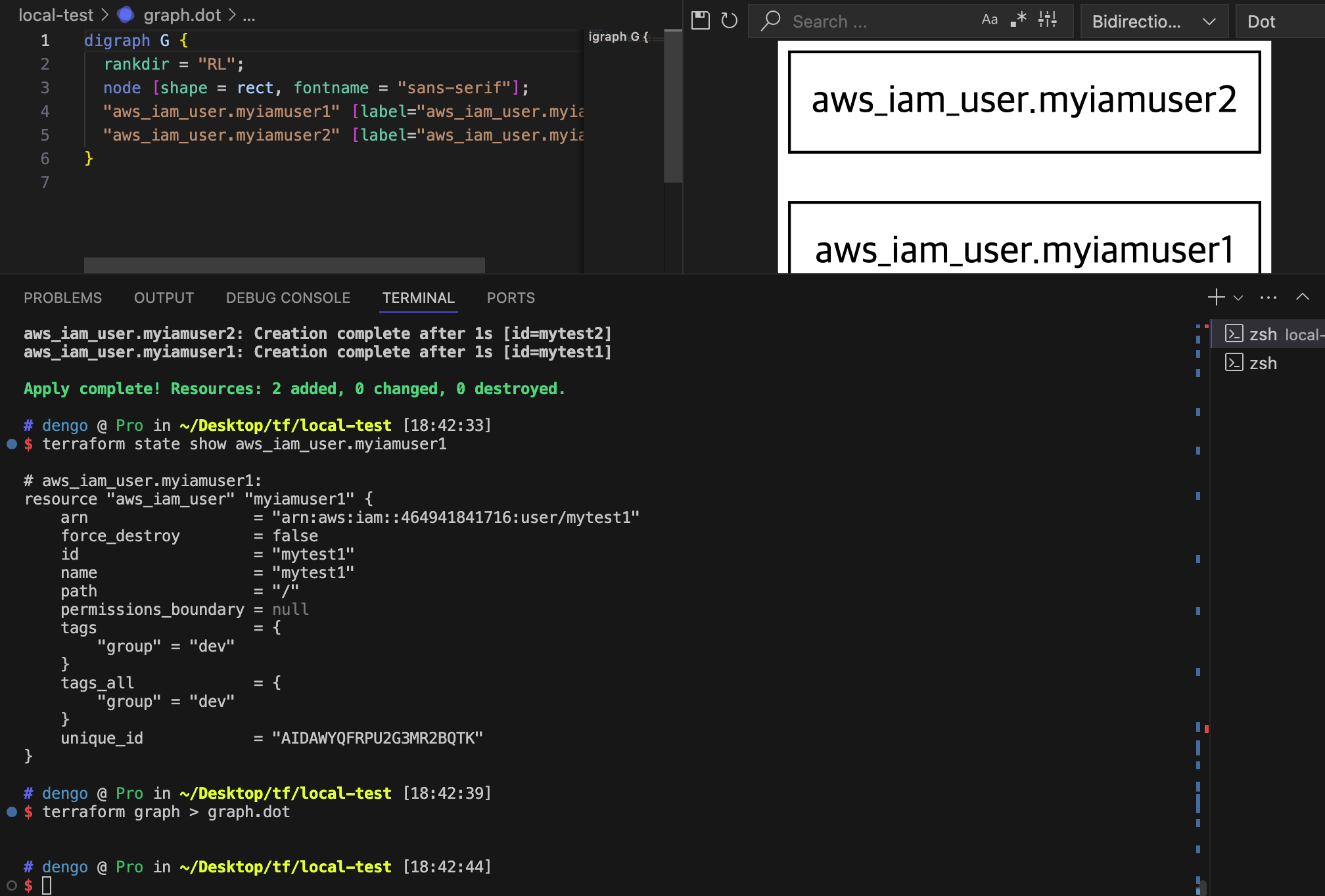
# graph 확인 > graph.dot 파일 선택 후 오른쪽 상단 DOT 클릭
terraform graph > graph.dot
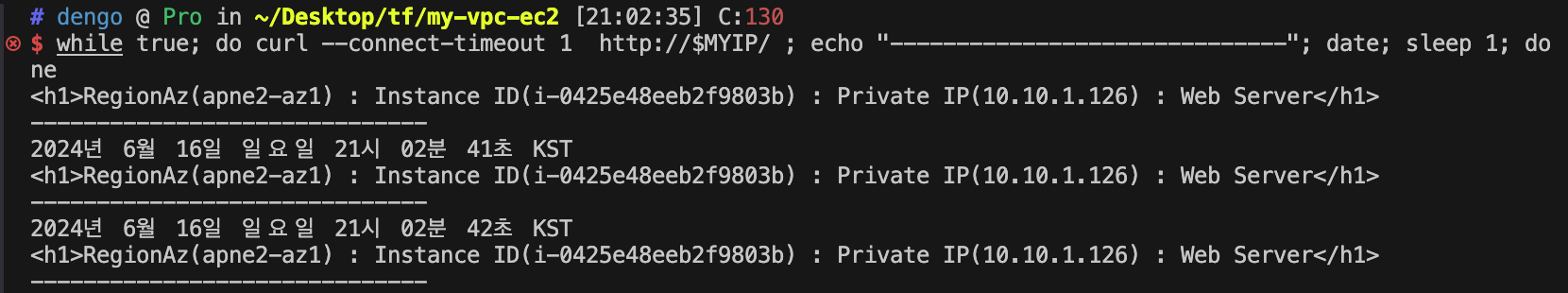
# 출력된 EC2 퍼블릭IP로 cul 접속 확인
terraform output -raw myec2_public_ip
52.79.154.3
MYIP=$(terraform output -raw myec2_public_ip)
while true; do curl --connect-timeout 1 http://$MYIP/ ; echo "------------------------------"; date; sleep 1; done
Local 지역 값
코드 내에서 사용자가 지정한 값 또는 속성 값을 가공해 참조 가능한 local (지역 값)은 외부에서 입력되지 않고, 코드 내에서만 가공되어 동작하는 값을 선언한다.
‘local’은 입력 변수와 달리 선언된 모듈 내에서만 접근 가능하고, 변수처럼 실행 시에 입력받을 수 없다.
로컬은 사용자가 테라폼 코드를 구현할 때 값이나 표현식을 반복적으로 사용할 수 있는 편의를 제공한다. 하지만 빈번하게 여러 곳에서 사용되는 경우 실제 값에 대한 추적이 어려워져 유지 관리 측면에서 부담이 발생할 수 있으므로 주의해야 한다.
- 로컬이 선언되는 블록은 locals로 시작한다. 선언되는 인수에 표현되는 값은 상수만이 아닌 리소스의 속성, 변수의 값들도 조합해 정의할 수 있다.
- 동일한 tf 파일 내에서 여러 번 선언하는 것도 가능하고 여러 파일에 걸쳐 만드는 것도 가능하다.
- 다만 lcoals에 선언한 로컬 변수 이름은 전체 루트 모듈 내에서 유일해야 한다.
- 정의되는 속성 값은 지정된 값의 형태에 따라 다양한 유형으로 정의할 수 있다.
- main.tf 파일 : local 값 선언 방식의 예
variable "prefix" {
default = "hello"
}
locals {
name = "terraform"
content = "${var.prefix} ${local.name}"
my_info = {
age = 20
region = "KR"
}
my_nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
locals {
content = "content2" # 중복 선언되었으므로 오류가 발생한다.
}
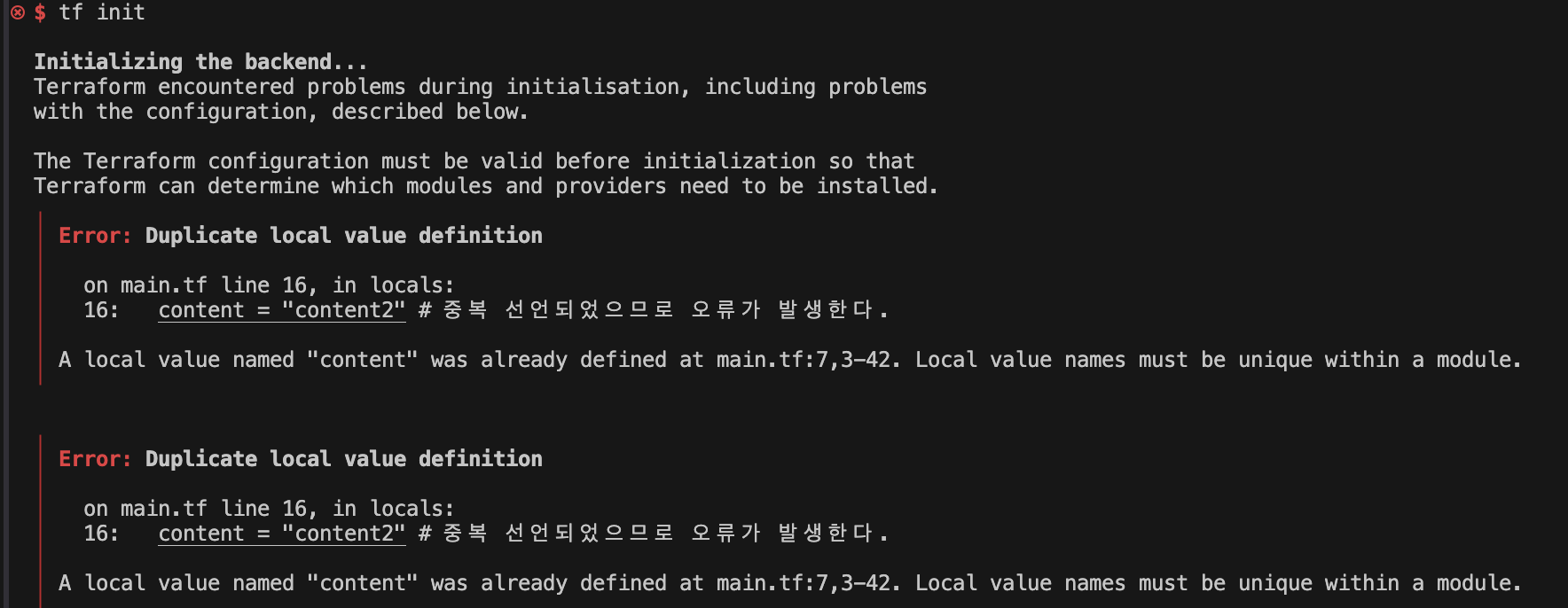
##파일 수정
variable "prefix" {
default = "hello"
}
locals {
name = "terraform"
content = "${var.prefix} ${local.name}"
my_info = {
age = 20
region = "KR"
}
my_nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
local 참조
- 선언된 local 값은 local.<이름>으로 참조할 수 있다.
- 테라폼 구성 파일을 여러 개 생성해 작업하는 경우 서로 다른 파일에 선언되어 있더라도 다른 파일에서 참조할 수 있다.
- main.tf 파일 내용 수정
variable "prefix" {
default = "hello"
}
locals {
name = "terraform"
}
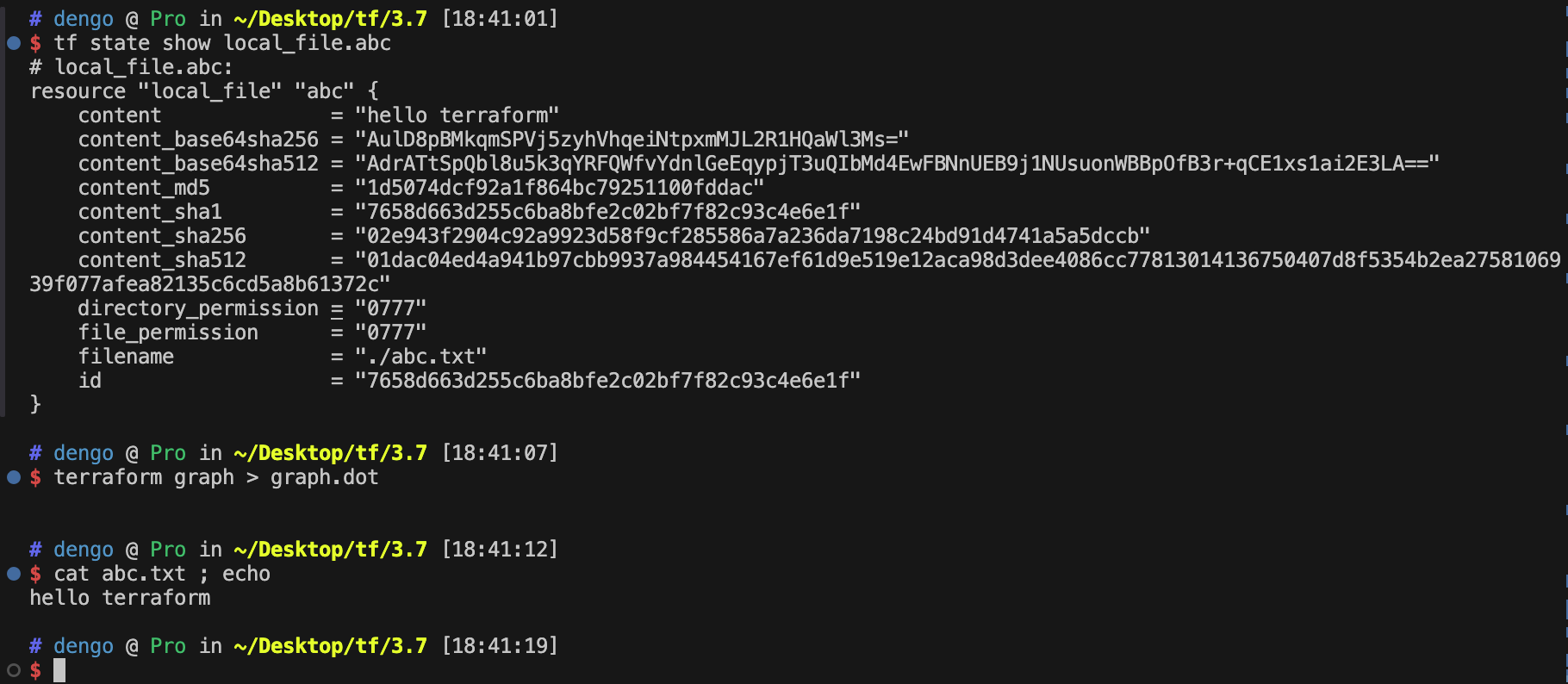
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = local.content
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}
---
- 선언된 local 값은 local.<이름>으로 참조할 수 있다.
- 테라폼 구성 파일을 여러 개 생성해 작업하는 경우 서로 다른 파일에 선언되어 있더라도 다른 파일에서 참조할 수 있다.
- main.tf 파일 내용 수정
variable "prefix" {
default = "hello"
}
locals {
name = "terraform"
}
resource "local_file" "abc" {
content = local.content
filename = "${path.module}/abc.txt"
}touch sub.tflocals {
content = "${var.prefix} ${local.name}"
}#
ls *.tf
terraform init -upgrade
terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
terraform state show local_file.abc
# graph 확인 > graph.dot 파일 선택 후 오른쪽 상단 DOT 클릭
terraform graph > graph.dot
#
cat abc.txt ; echo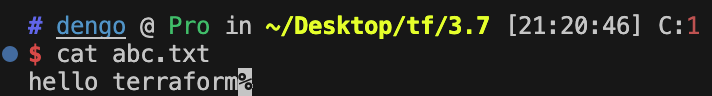
(추가) terraform.tfvars에 정의된 변수 선언
#
echo 'prefix="t101-study"' > terraform.tfvars
cat terraform.tfvars
#
terraform apply -auto-approve
cat abc.txt ; echo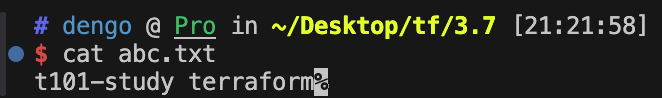
[스터디 전용/실습2] AWS IAM User 생성 - tutorials
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-northeast-2"
}
locals {
name = "mytest"
team = {
group = "dev"
}
}
resource "aws_iam_user" "myiamuser1" {
name = "${local.name}1"
tags = local.team
}
resource "aws_iam_user" "myiamuser2" {
name = "${local.name}2"
tags = local.team
}
#
terraform init && terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform state list
terraform state show aws_iam_user.myiamuser1
terraform state show aws_iam_user.myiamuser2
# graph 확인 > graph.dot 파일 선택 후 오른쪽 상단 DOT 클릭
terraform graph > graph.dot
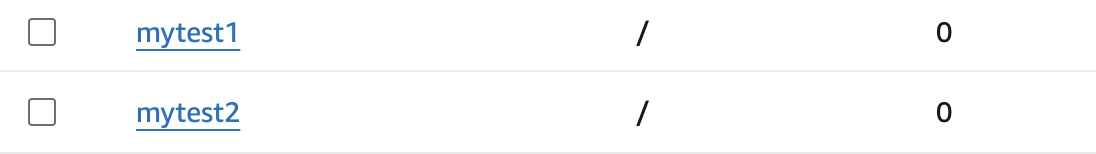
# iam 사용자 리스트 확인
aws iam list-users | jq
# 삭제
terraform destroy -auto-approve -target=aws_iam_user.myiamuser1
terraform state list
terraform destroy -auto-approve
terraform state list'study > T101 4기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| T101 4기 3주차 첫번째 (0) | 2024.06.29 |
|---|---|
| T101 4기 2주차 두번째 (0) | 2024.06.22 |
| T101 4기 1주차 세번째 (0) | 2024.06.15 |
| T101 4기 1주차 두번째 (0) | 2024.06.15 |
| T101 4기 1주차 첫번째 (0) | 2024.06.15 |



