요즘 매우 핫하는 GatewayAPI에 대해서 공부해보겠습니다!
Gateway API
Gateway API 소개 : 기존의 Ingress 에 좀 더 기능을 추가, 역할 분리(role-oriented) - Docs
Gateway API
Gateway API is a family of API kinds that provide dynamic infrastructure provisioning and advanced traffic routing.
kubernetes.io
- 서비스 메시(istio)에서 제공하는 Rich 한 기능 중 일부 기능들과 혹은 운영 관리에 필요한 기능들을 추가
- 추가 기능 : 헤더 기반 라우팅, 헤더 변조, 트래픽 미러링(쉽게 트래픽 복제), 역할 기반

아래 핸드온으로 학습하면 큰 도움이 될 듯 합니다.
[Tutorial] Hands-On with the Kubernetes Gateway API and Envoy Proxy - Blog Github
solo-blog/gateway-api-tutorial at main · solo-io/solo-blog
solo.io/blog resources. Contribute to solo-io/solo-blog development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
구성요소
- GatewayClass,Gateway, HTTPRoute, TCPRoute, Service


Request flow

Why does a role-oriented API matter?

Install KinD Cluster
#
cat <<EOT> kind-1node.yaml
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30000
hostPort: 30000
- containerPort: 30001
hostPort: 30001
- containerPort: 30002
hostPort: 30002
EOT
# Install KinD Cluster
kind create cluster --image kindest/node:v1.30.0 --config kind-1node.yaml --name myk8s
# 노드에 기본 툴 설치
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane sh -c 'apt update && apt install tree psmisc lsof wget bsdmainutils bridge-utils net-tools dnsutils tcpdump ngrep iputils-ping git vim -y'
# 노드/파드 확인
kubectl get nodes -o wide
kubectl get pod -A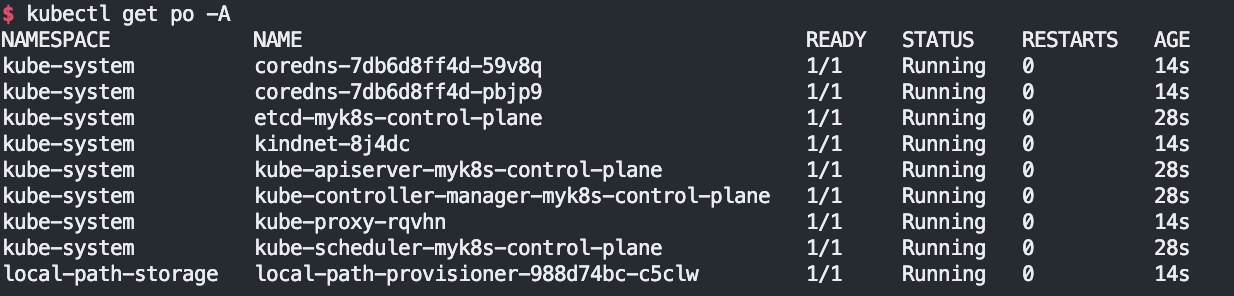
Install Gateway API CRDs : The Kubernetes Gateway API abstractions are expressed using Kubernetes CRDs.
# CRDs 설치 및 확인
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.0.0/standard-install.yaml
kubectl get crd
Install Glooctl Utility : GLOOCTL is a command-line utility that allows users to view, manage, and debug Gloo Gateway deployments - Link
:: Gloo Edge Docs
Navigation : Getting Started What is Gloo Gateway? Setup - Preparation - Platform Configuration - Gloo Gateway - Gloo Gateway as an Ingress Controller - Installing Gloo Gateway Enterprise - Gloo Gateway Federation - Advanced Configuration - Guides Operatio
docs.solo.io
# [신규 터미널] 아래 bash 진입 후 glooctl 툴 사용
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane bash
----------------------------------------
# Install Glooctl Utility
## glooctl install gateway # install gloo's function gateway functionality into the 'gloo-system' namespace
## glooctl install ingress # install very basic Kubernetes Ingress support with Gloo into namespace gloo-system
## glooctl install knative # install Knative serving with Gloo configured as the default cluster ingress
## curl -sL https://run.solo.io/gloo/install | sh
curl -sL https://run.solo.io/gloo/install | GLOO_VERSION=v1.17.7 sh
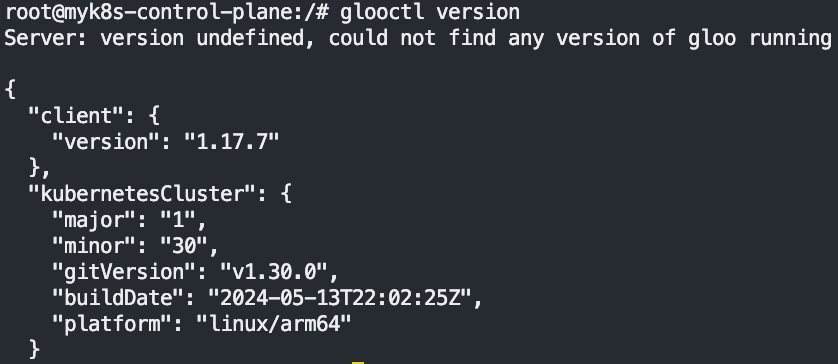
export PATH=$HOME/.gloo/bin:$PATH
# 버전 확인
glooctl version
----------------------------------------
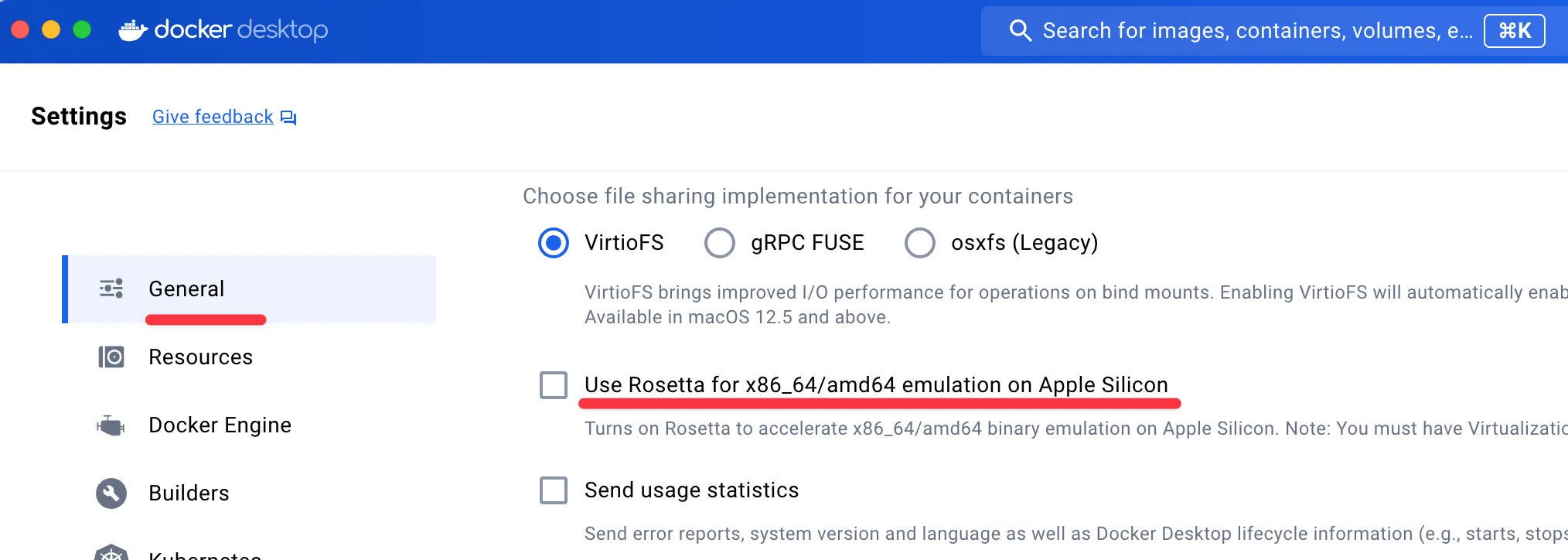
Install Gloo Gateway : 오픈소스 버전
- macOS Docker Desktop : 아래 옵션 Uncheck 해둘 것 → Apply & restart
# [신규 터미널] 모니터링
watch -d kubectl get pod,svc,endpointslices,ep -n gloo-system
# Install Gloo Gateway
helm repo add gloo https://storage.googleapis.com/solo-public-helm
helm repo update
helm install -n gloo-system gloo-gateway gloo/gloo \
--create-namespace \
--version 1.17.7 \
--set kubeGateway.enabled=true \
--set gloo.disableLeaderElection=true \
--set discovery.enabled=false
# Confirm that the Gloo control plane has successfully been deployed using this command
kubectl rollout status deployment/gloo -n gloo-system
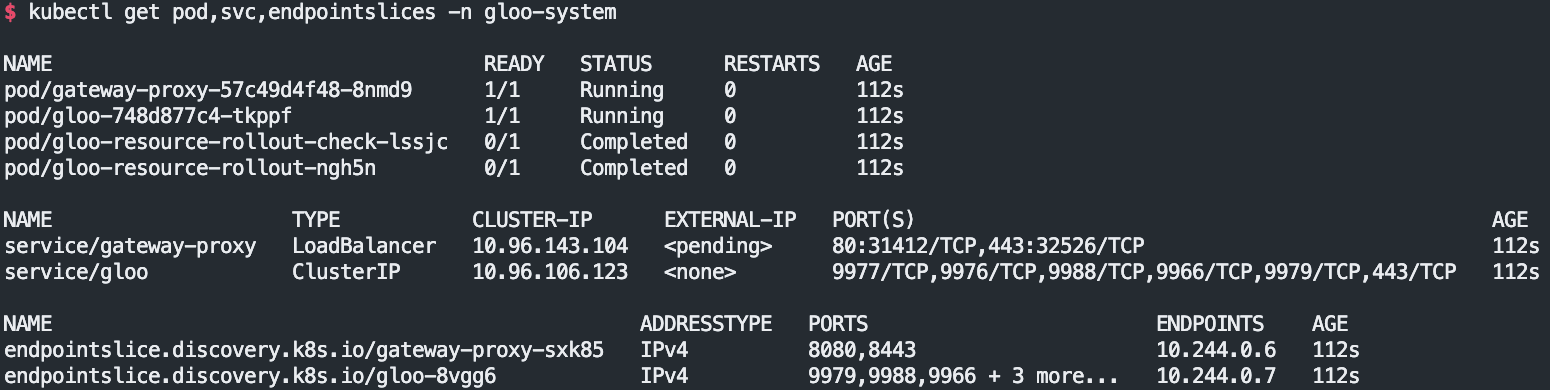
# 설치 확인
kubectl get crd | grep 'networking.k8s.io'
kubectl get crd | grep -v 'networking.k8s.io'
kubectl get pod,svc,endpointslices -n gloo-system
#
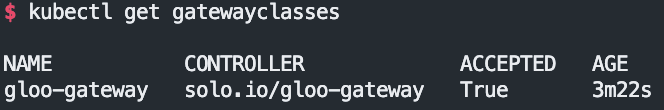
kubectl explain gatewayclasses
kubectl get gatewayclasses
NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE
gloo-gateway solo.io/gloo-gateway True 21m
kubectl get gatewayclasses -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
labels:
app: gloo
name: gloo-gateway
spec:
controllerName: solo.io/gloo-gateway
...
Install Httpbin Application : A simple HTTP Request & Response Service - Link
httpbin.org
A simple HTTP Request & Response Service. Run locally: $ docker run -p 80:80 kennethreitz/httpbin
httpbin.org
#
watch -d kubectl get pod,svc,endpointslices,ep -n httpbin
# Install Httpbin Application
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/solo-blog/main/gateway-api-tutorial/01-httpbin-svc.yaml
# 설치 확인
kubectl get deploy,pod,svc,endpointslices,sa -n httpbin
kubectl rollout status deploy/httpbin -n httpbin
# (옵션) NodePort 설정
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: httpbin
service: httpbin
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 8000
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30000
selector:
app: httpbin
EOF
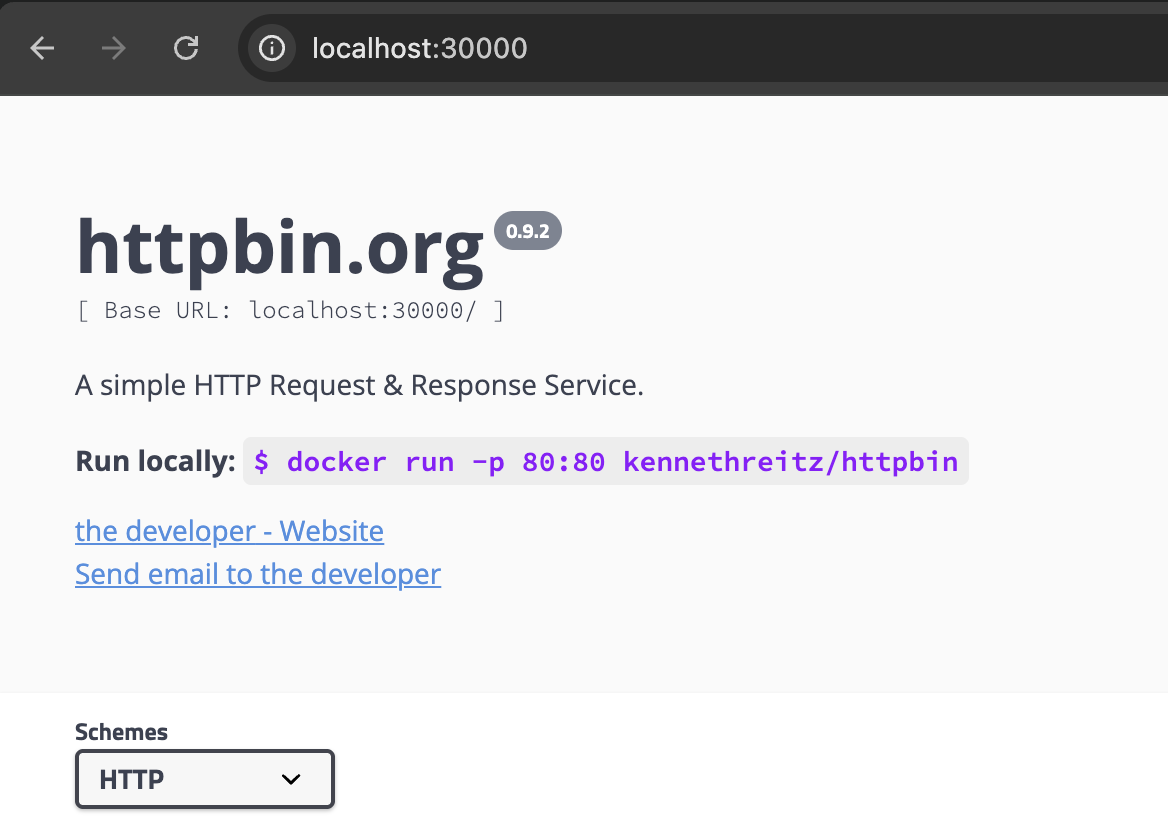
# (옵션) 로컬 접속 확인
echo "httpbin web - http://localhost:30000" # macOS 사용자
echo "httpbin web - http://192.168.50.10:30000" # Windows 사용자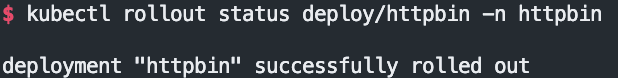
확인
Configure a Gateway Listener
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/02-gateway.yaml
# 확인 : Now we can confirm that the Gateway has been activated
kubectl get gateway -n gloo-system
kubectl get gateway -n gloo-system -o yaml | k neat
apiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: http
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
gatewayClassName: gloo-gateway
listeners:
- allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
name: http
port: 8080
protocol: HTTP
...
# You can also confirm that Gloo Gateway has spun up an Envoy proxy instance in response to the creation of this Gateway object by deploying gloo-proxy-http:
kubectl get deployment gloo-proxy-http -n gloo-system
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
gloo-proxy-http 1/1 1 1 5m22s
# envoy 사용 확인
kubectl get pod -n gloo-system
kubectl describe pod -n gloo-system |grep Image:
Image: quay.io/solo-io/gloo-envoy-wrapper:1.17.7
Image: quay.io/solo-io/gloo:1.17.7
Image: quay.io/solo-io/gloo-envoy-wrapper:1.17.7
# gloo-proxy-http 서비스는 External-IP는 Pending 상태
kubectl get svc -n gloo-system gloo-proxy-http
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
gloo-proxy-http LoadBalancer 10.96.71.22 <pending> 8080:31555/TCP 2m4s
# gloo-proxy-http NodePort 30001 설정
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: http
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/name: gloo-proxy-http
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.17.7
gateway.networking.k8s.io/gateway-name: http
gloo: kube-gateway
helm.sh/chart: gloo-gateway-1.17.7
name: gloo-proxy-http
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
ports:
- name: http
nodePort: 30001
port: 8080
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: http
app.kubernetes.io/name: gloo-proxy-http
gateway.networking.k8s.io/gateway-name: http
type: LoadBalancer
EOF
kubectl get svc -n gloo-system gloo-proxy-http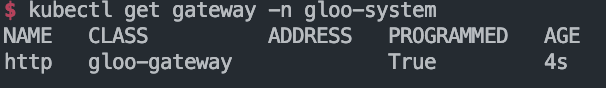
노드 포트 변경

이제 HTTP ROUTE를 보자

HTTPRoute Spec
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
labels:
example: httpbin-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: http
namespace: gloo-system
hostnames:
- "api.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Exact
value: /get
backendRefs:
- name: httpbin
port: 8000
The Gateway object simply represents a host:port listener that the proxy will expose to accept ingress traffic.
# Our route watches for HTTP requests directed at the host api.example.com with the request path /get and then forwards the request to the httpbin service on port 8000.
# Let’s establish this route now:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/03-httpbin-route.yaml
#
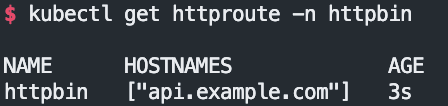
kubectl get httproute -n httpbin
NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
httpbin ["api.example.com"] 3m15s
kubectl describe httproute -n httpbin
...
Spec:
Hostnames:
api.example.com
Parent Refs:
Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
Kind: Gateway
Name: http
Namespace: gloo-system
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: httpbin
Port: 8000
Weight: 1
Matches:
Path:
Type: Exact
Value: /get
...
Test the Simple Route with Curl
# let’s use curl to display the response with the -i option to additionally show the HTTP response code and headers.
echo "127.0.0.1 api.example.com" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:30001/get" # 웹브라우저
혹은
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/get # kubectl port-forward 사용 시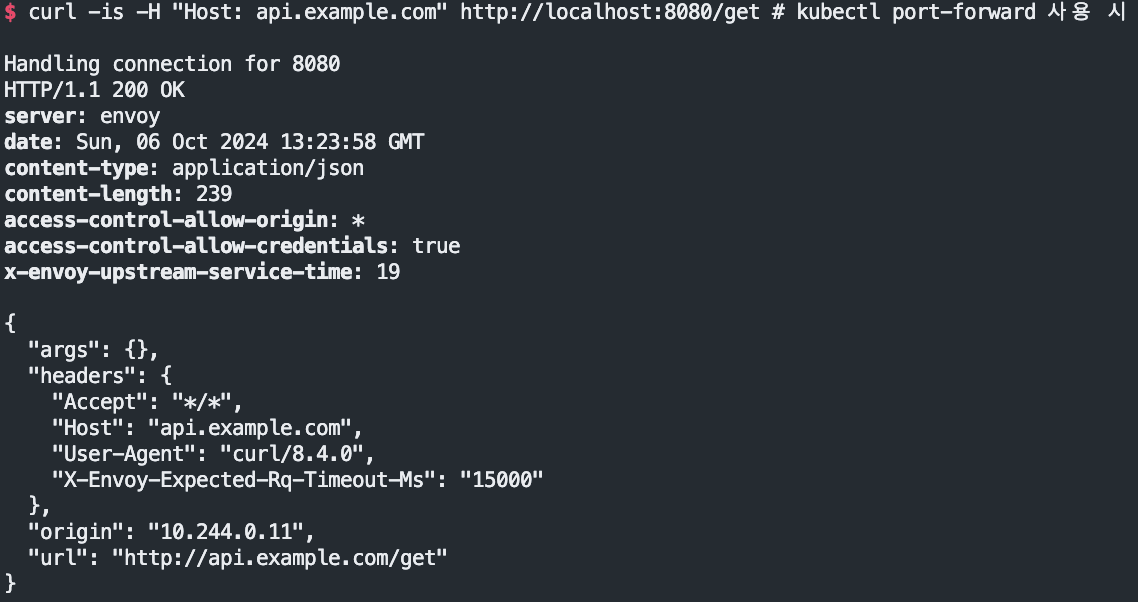
아래의 호출은 왜 이런걸까?
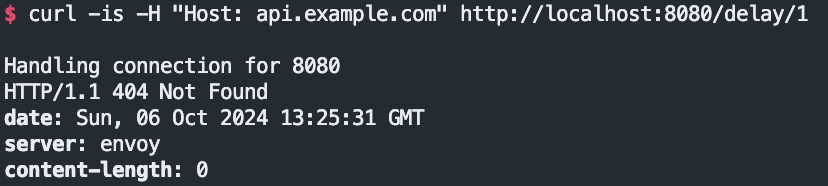
아래와 같은 role이 있기 때문
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Exact
value: /get
[정규식 패턴 매칭] Explore Routing with Regex Matching Patterns
Let’s assume that now we DO want to expose other httpbin endpoints like /delay. Our initial HTTPRoute is inadequate, because it is looking for an exact path match with /get.
예시) /api/httpbin/delay/1 ⇒ /delay/1
# Here are the modifications we’ll apply to our HTTPRoute:
- matches:
# Switch from an Exact Matcher(정확한 매팅) to a PathPrefix (경로 매팅) Matcher
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api/httpbin/
filters:
# Replace(변경) the /api/httpbin matched prefix with /
- type: URLRewrite
urlRewrite:
path:
type: ReplacePrefixMatch
replacePrefixMatch: /
-2가지 수정 내용 적용 후 확인
#
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/04-httpbin-rewrite.yaml
# 확인
kubectl describe httproute -n httpbin
...
Spec:
Hostnames:
api.example.com
Parent Refs:
Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
Kind: Gateway
Name: http
Namespace: gloo-system
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: httpbin
Port: 8000
Weight: 1
Filters:
Type: URLRewrite
URL Rewrite:
Path:
Replace Prefix Match: /
Type: ReplacePrefixMatch
Matches:
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /api/httpbin/
Test Routing with Regex Matching Patterns
#
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:30001/api/httpbin/get" # 웹브라우저
혹은
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/httpbin/get # kubectl port-forward 사용 시
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
server: envoy
date: Sun, 06 Oct 2024 08:08:09 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 289
access-control-allow-origin: *
access-control-allow-credentials: true
x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 18 # envoy 가 업스트림 httpbin 요청 처리에 걸리 시간 0.018초
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "api.example.com",
"User-Agent": "curl/8.7.1",
"X-Envoy-Expected-Rq-Timeout-Ms": "15000",
"X-Envoy-Original-Path": "/api/httpbin/get"
},
"origin": "10.244.0.11",
"url": "http://api.example.com/get"
}
# 아래 NodePort 와 GW API 통한 접속 비교
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:30001/api/httpbin/get"
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:30000/api/httpbin/get"
---
#
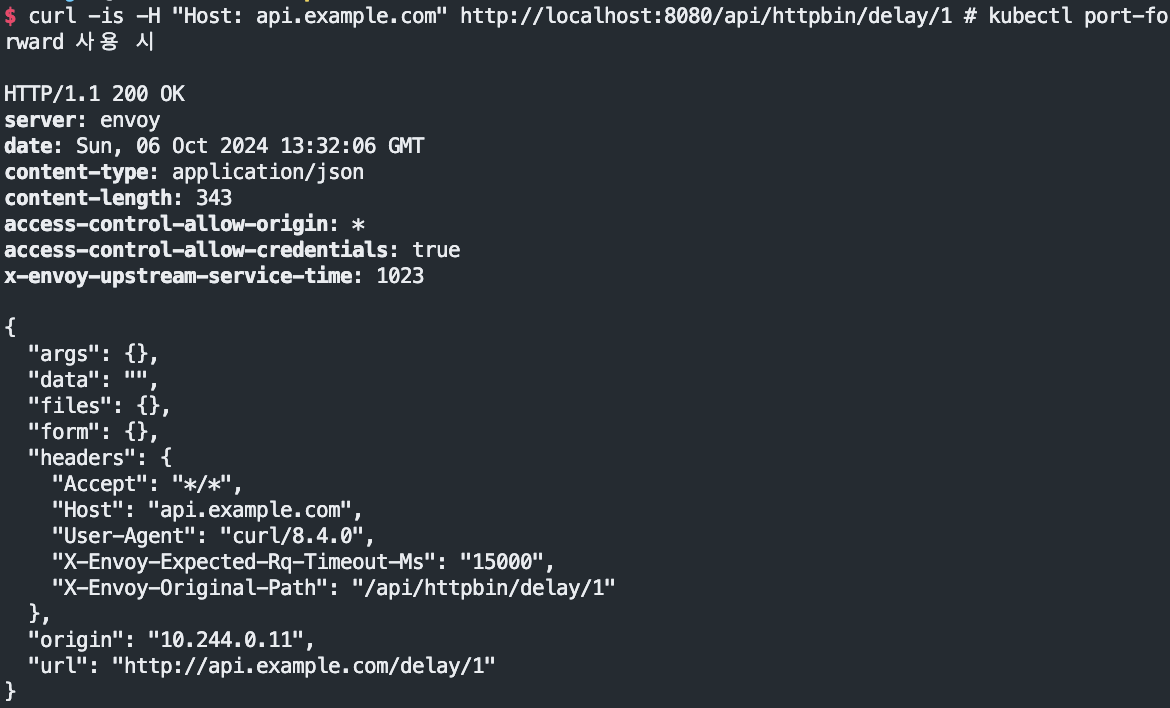
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:30001/api/httpbin/delay/1" # 웹브라우저
혹은
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/httpbin/delay/1 # kubectl port-forward 사용 시
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/httpbin/delay/2
#
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:31001/api/httpbin/delay/1"
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:31000/api/httpbin/delay/1"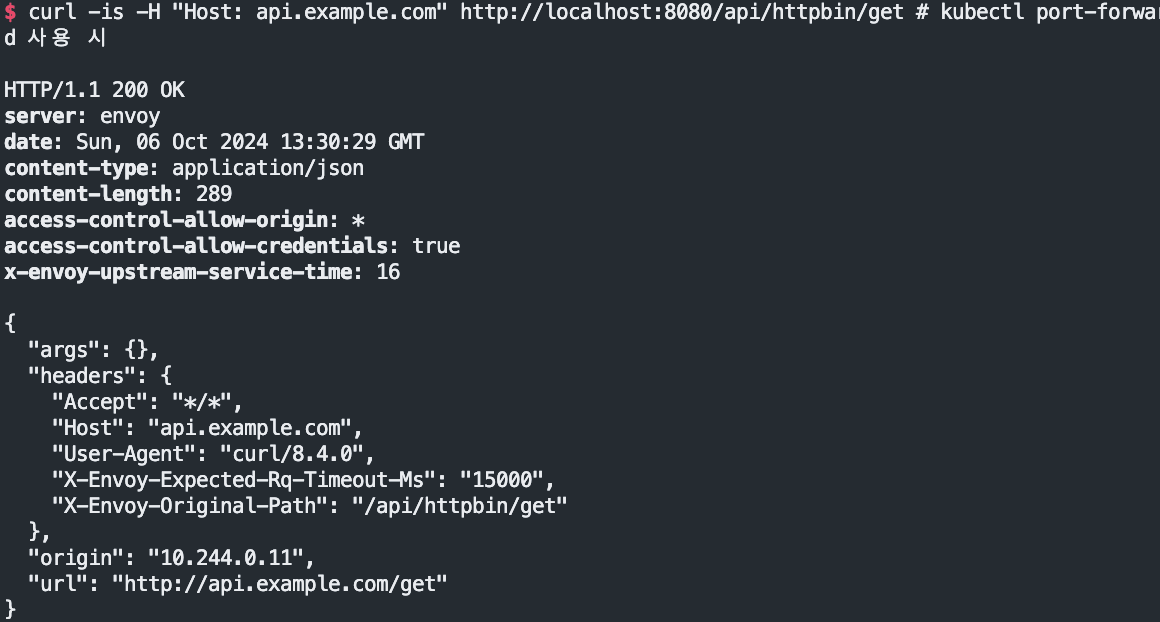
delay check
[업스트림 베어러 토큰을 사용한 변환] Test Transformations with Upstream Bearer Tokens
목적 : 요청을 라우팅하는 백엔드 시스템 중 하나에서 인증해야 하는 요구 사항이 있는 경우는 어떻게 할까요? 이 업스트림 시스템에는 권한 부여를 위한 API 키가 필요하고, 이를 소비하는 클라이언트에 직접 노출하고 싶지 않다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 즉, 프록시 계층에서 요청에 주입할 간단한 베어러 토큰을 구성하고 싶습니다. (정적 API 키 토큰을 직접 주입)
# The new filters stanza in our HTTPRoute now looks like this:
filters:
- type: URLRewrite
urlRewrite:
path:
type: ReplacePrefixMatch
replacePrefixMatch: /
# Add a Bearer token to supply a static API key when routing to backend system
- type: RequestHeaderModifier
requestHeaderModifier:
add:
- name: Authorization
value: Bearer my-api-key#
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/05-httpbin-rewrite-xform.yaml
#
kubectl describe httproute -n httpbin
...
Spec:
...
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: httpbin
Port: 8000
Weight: 1
Filters:
Type: URLRewrite
URL Rewrite:
Path:
Replace Prefix Match: /
Type: ReplacePrefixMatch
Request Header Modifier:
Add:
Name: Authorization
Value: Bearer my-api-key
Type: RequestHeaderModifier
Matches:
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /api/httpbin/
동작 테스트
#
echo "httproute - http://api.example.com:30001/api/httpbin/get" # 웹브라우저
혹은
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/httpbin/get # kubectl port-forward 사용 시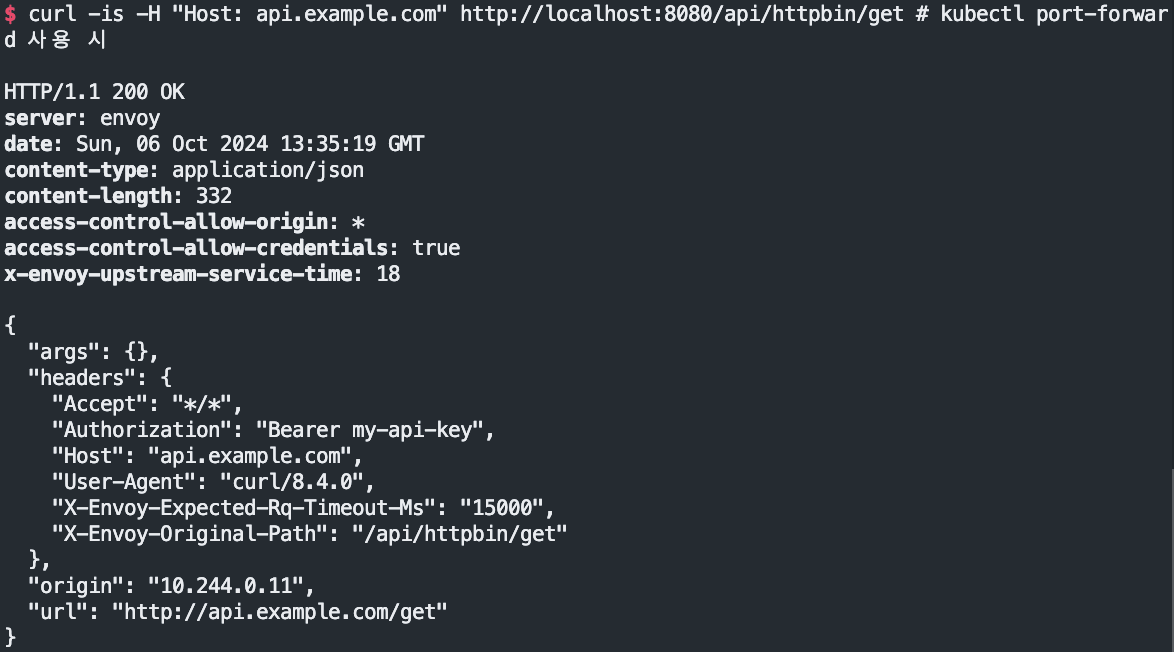
라우팅 전략(migratie)
# You should see the response below, indicating deployments for both v1 and v2 of my-workload have been created in the my-workload namespace.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/06-workload-svcs.yaml
# v1,v2 2가지 버전 워크로드 확인
kubectl get deploy,pod,svc,endpointslices -n my-workload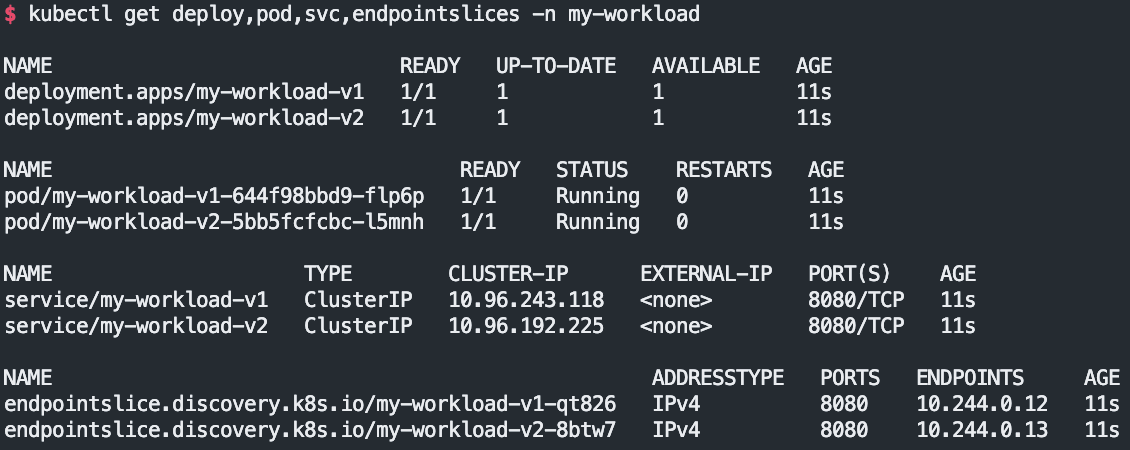
Test Simple V1 Routing
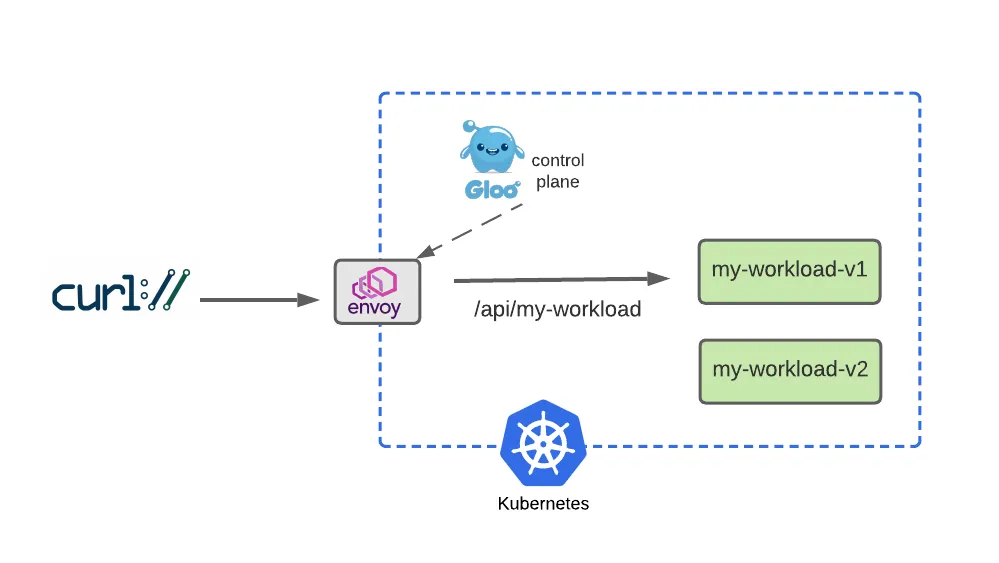
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: my-workload
namespace: my-workload
labels:
example: my-workload-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: http
namespace: gloo-system
hostnames:
- "api.example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api/my-workload
backendRefs:
- name: my-workload-v1
namespace: my-workload
port: 8080
Now apply this route:
#
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/07-workload-route.yaml
#
kubectl get httproute -A
NAMESPACE NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
httpbin httpbin ["api.example.com"] 41m
my-workload my-workload ["api.example.com"] 39s
#
kubectl describe httproute -n my-workload
...
Spec:
Hostnames:
api.example.com
Parent Refs:
Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
Kind: Gateway
Name: http
Namespace: gloo-system
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: my-workload-v1
Namespace: my-workload
Port: 8080
Weight: 1
Matches:
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /api/my-workload#
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload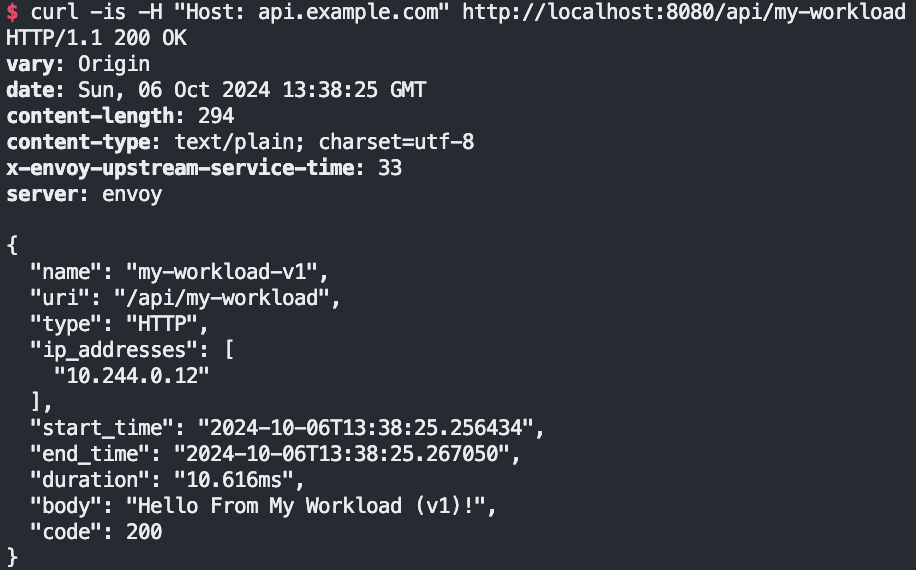
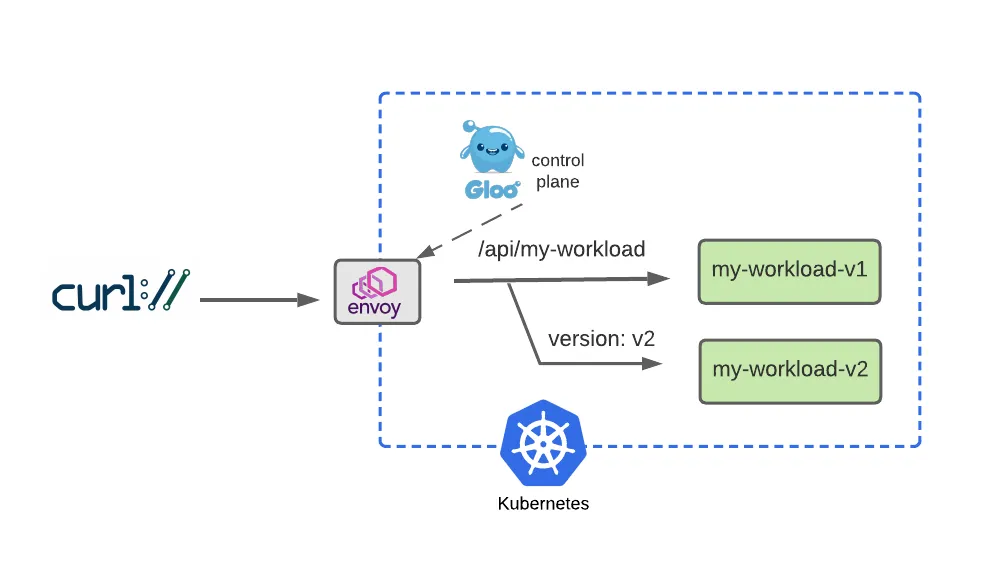
Simulate a v2 Dark Launch with Header-Based Routing
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api/my-workload
# Add a matcher to route requests with a v2 version header to v2
# version=v2 헤더값이 있는 사용자만 v2 라우팅
headers:
- name: version
value: v2
backendRefs:
- name: my-workload-v2
namespace: my-workload
port: 8080
- matches:
# Route requests without the version header to v1 as before
# 대다수 일반 사용자는 기존 처럼 v1 라우팅
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api/my-workload
backendRefs:
- name: my-workload-v1
namespace: my-workload
port: 8080
Configure two separate routes, one for v1 that the majority of service consumers will still use, and another route for v2 that will be accessed by specifying a request header with name version and value v2. Let’s apply the modified HTTPRoute:
#
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/08-workload-route-header.yaml
#
kubectl describe httproute -n my-workload
...
Spec:
...
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: my-workload-v2
Namespace: my-workload
Port: 8080
Weight: 1
Matches:
Headers:
Name: version
Type: Exact
Value: v2
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /api/my-workload
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: my-workload-v1
Namespace: my-workload
Port: 8080
Weight: 1
Matches:
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /api/my-workload# Now we’ll test the original route, with no special headers supplied, and confirm that traffic still goes to v1:
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload | grep body
"body": "Hello From My Workload (v1)!",
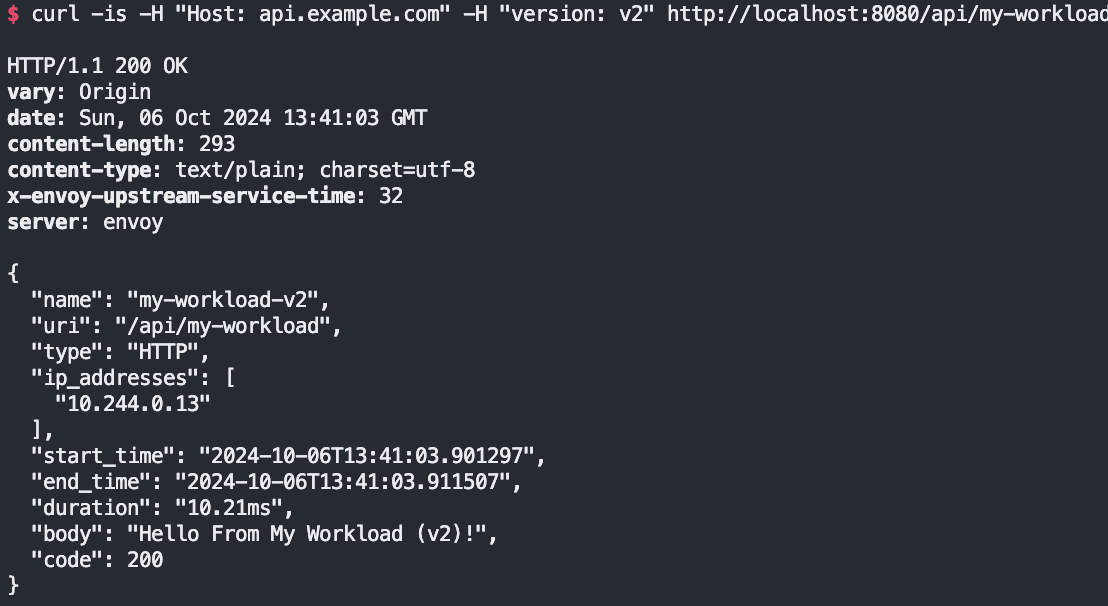
# But it we supply the version: v2 header, note that our gateway routes the request to v2 as expected:
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" -H "version: v2" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" -H "version: v2" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload | grep body
version2 로 접근
테스트가 완료되었으니 이제 version2에도 트레픽을 주입

# Apply this 50-50 routing policy with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/09-workload-route-split.yaml
#
kubectl describe httproute -n my-workload
...# 반복 접속 후 대략 비률 확인
for i in {1..100}; do curl -s -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload/ | grep body; done | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr
for i in {1..200}; do curl -s -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload/ | grep body; done | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr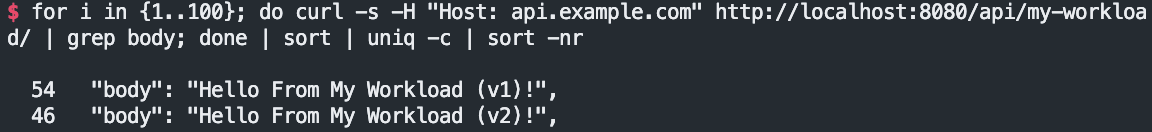
디버그해보기
-my-bad-workload-v2 업스트림 구성의 오타를 시뮬레이션하여 올바른 타겟팅하는 대신 존재하지 않는 백엔드 서비스를 타겟팅하도록 변경
# [신규 터미널] 모니터링
kubectl get httproute -n my-workload my-workload -o yaml -w
#
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/10-workload-route-split-bad-dest.yaml
#
kubectl describe httproute -n my-workload
...
Spec:
Hostnames:
api.example.com
Parent Refs:
Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
Kind: Gateway
Name: http
Namespace: gloo-system
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: my-workload-v1
Namespace: my-workload
Port: 8080
Weight: 50
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: my-bad-workload-v2
Namespace: my-workload
Port: 8080
Weight: 50
Matches:
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /api/my-workload
Status:
Parents:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2024-10-06T08:38:25Z
Message: Service "my-bad-workload-v2" not found
Observed Generation: 4
Reason: BackendNotFound
Status: False
Type: ResolvedRefs
Last Transition Time: 2024-10-06T08:25:47Z
Message:
Observed Generation: 4
Reason: Accepted
Status: True
Type: Accepted
Controller Name: solo.io/gloo-gateway
Parent Ref:
Group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
Kind: Gateway
Name: http
Namespace: gloo-system#
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload
curl -is -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
date: Wed, 03 Jul 2024 08:21:11 GMT
server: envoy
content-length: 0
#
for i in {1..100}; do curl -s -H "Host: api.example.com" http://localhost:8080/api/my-workload/ | grep body; done | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr
이렇게 안 된다

이제 디버그를 아래와 같이 해보자
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane
-----------------------------------
export PATH=$HOME/.gloo/bin:$PATH
glooctl check
Checking Gateways... OK
Checking Proxies... 1 Errors!
Detected Kubernetes Gateway integration!
Checking Kubernetes GatewayClasses... OK
Checking Kubernetes Gateways... OK
Checking Kubernetes HTTPRoutes... 1 Errors!
Skipping Gloo Instance check -- Gloo Federation not detected.
Error: 2 errors occurred:
* Found proxy with warnings by 'gloo-system': gloo-system gloo-system-http
Reason: warning:
Route Warning: InvalidDestinationWarning. Reason: invalid destination in weighted destination list: *v1.Upstream { blackhole_ns.kube-svc:blackhole-ns-blackhole-cluster-8080 } not found
* HTTPRoute my-workload.my-workload.http status (ResolvedRefs) is not set to expected (True). Reason: BackendNotFound, Message: Service "my-bad-workload-v2" not found
# 원인 관련 정보 확인
kubectl get httproute my-workload -n my-workload -o yaml
...
status:
parents:
- conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-11-28T21:09:20Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 6
reason: BackendNotFound
status: "False"
type: ResolvedRefs
...
# 정상 설정으로 해결 configuration is again clean.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-gateway-use-cases/main/gateway-api-tutorial/09-workload-route-split.yaml
kubectl get httproute my-workload -n my-workload -o yaml
#
glooctl check
...'study > KANS 3기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| KANS 3기 Istio (0) | 2024.10.19 |
|---|---|
| KANS 3기 Istio KIND 실습환경 구축 (1) | 2024.10.19 |
| KANS 3기 6주차 첫번째 (0) | 2024.10.12 |
| KANS 3기 5주차 첫번째 (2) | 2024.10.04 |
| KANS 3기 5주차 두번째 (0) | 2024.10.04 |



